Design Overview
In the following diagrams and tables, the design of the adjacent construction is described. Please pay particular attention to the connection areas, as any deviation will affect the overall accuracy and rigidity of the roller bearing.
To avoid degradation of bearing friction torque, accuracy requirements, and operating characteristics, the recommended tolerances must not be exceeded.
Important Note
myonic AXCR bearing bore and outer diameter are manufactured according to P5/DIN 620 standard with strict tolerance limits. This helps create precise fits, and the bearing accuracy can be transferred to the table.
Fit Type Description
Press Fit (Interference Fit)
In principle, when the fit is too tight, radial bearing preload increases, therefore:
The Following Will Increase
- Surface pressure in the raceway
- Bearing friction
- Bearing heat generation
- Wear amount
The Following Will Decrease
- Maximum speed
- Service life
Clearance Fit
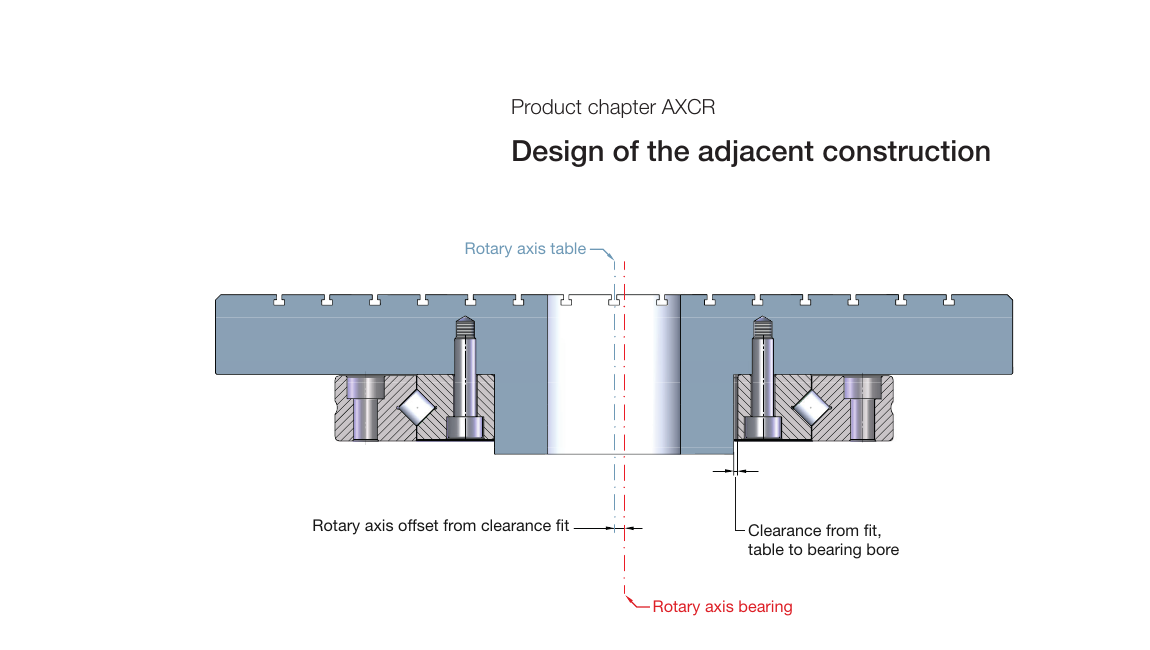
If the rotating ring is not supported in a clearance fit, the raceway of the rotating shaft may shift relative to the table center. The clearance from the fit table to the bearing bore (also applicable for the clearance from bearing OD to table for rotating outer ring) may increase radial runout.
Applications with Lower Accuracy Requirements
In applications with lower accuracy requirements, the ring can also be fastened with screws in a clearance fit. The wall thickness of the table adapter in the bearing bore (or OD) must be large enough to exclude the risk of uncertain operating conditions such as vibration, radial runout errors, and repeatability.
Centered Shafts / Tables
Centering can be performed with a shaft clearance fit to the rotating shaft. Due to the solid ring, AXCR bearings are less sensitive to non-positive locking shafts than AXRY bearings. However, reduced shaft rigidity and possible radial runout problems or rotating shaft displacement during overload must be accepted.
Radial Runout Measurement Note
Radial runout measurements using a centering table and installed measuring ball do not match the following catalog values. In this precisely centered measurement, only the radial runout of the raceway and the shape error of the measuring structure are measured. If the measuring structure is executed precisely, the measured values will be lower than the specified myonic radial runout values. myonic radial runout values include the radial runout error of the raceway and the roundness of the bore.
Fastening Possibilities
Fastening Possibilities AXCR-U / AXCR-S
myonic offers the following fastening methods in the standard series:
SA = Grooves Opposite
For connection dimensions, two cases need to be considered. For fastening method SA, since the two rings are offset from each other, there is no collision with the adjacent construction, so there are no specific connection dimension requirements.
SS = Grooves Identical
For fastening method SS, there is no offset between the inner and outer rings, so the specified table values apply. The diameter value da is the maximum, and the diameter value Di is the minimum.
Special Features
These two standard designs contain completely identical individual rings. Depending on the required fastening method, only one inner ring installed in a mirrored manner is installed.
The individual rings are always unsupported on the cylindrical counterbore side, meaning no collision occurs in fastening method "SA".
On the other hand, if ring arrangement "SS" is selected, a lower overall height results because the two recessed cylindrical counterbores are on the same side.
Offset "V" Precision Manufacturing
The offset "V" as shown in detail "X" can be manufactured with tolerances of a few micrometers according to customer requirements. This means that complex shim rings and high assembly costs are no longer required.
Recommended Connection Dimensions
Recommended Connection Dimensions (applicable for fastening method SS)
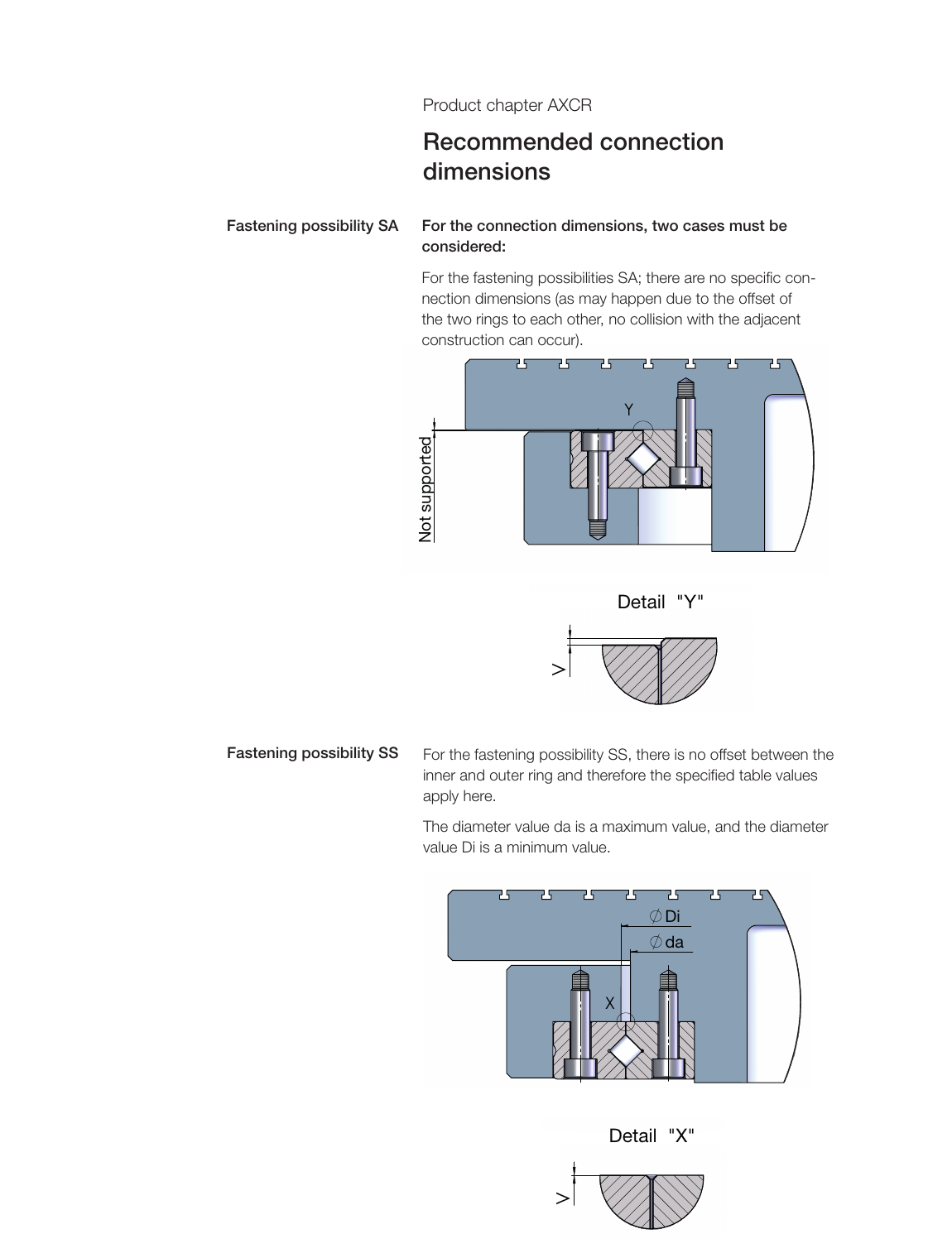
The following connection dimensions apply to fastening method SS (Grooves Identical):
| Cross Roller Bearing | Connection Dimension Ø da MAX [mm] | Connection Dimension Ø Di MIN [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| AXCR 80-U | 122.0 | 130.0 |
| AXCR 90-U | 144.5 | 152.5 |
| AXCR 115-U | 173.0 | 181.0 |
| AXCR 160-U | 223.0 | 231.0 |
| AXCR 210-U | 295.0 | 303.0 |
| AXCR 270-U | 331.0 | 339.0 |
| AXCR 350-U | 439.0 | 447.0 |
| AXCR 360-U | 450.0 | 458.0 |
| AXCR 540-U | 626.0 | 634.0 |
| AXCR 130-S | 162.0 | 170.0 |
| AXCR 150-S | 184.5 | 192.5 |
| AXCR 180-S | 213.0 | 221.0 |
| AXCR 220-S | 253.0 | 261.0 |
| AXCR 280-S | 315.0 | 323.0 |
| AXCR 360-S | 394.5 | 402.5 |
Dimension Symbol Legend
- da MAX - Maximum shaft diameter (safe distance to inner ring groove)
- Di MIN - Minimum housing bore diameter (safe distance to outer ring groove)
Recommended Minimum Wall Thicknesses
Recommended Minimum Wall Thicknesses
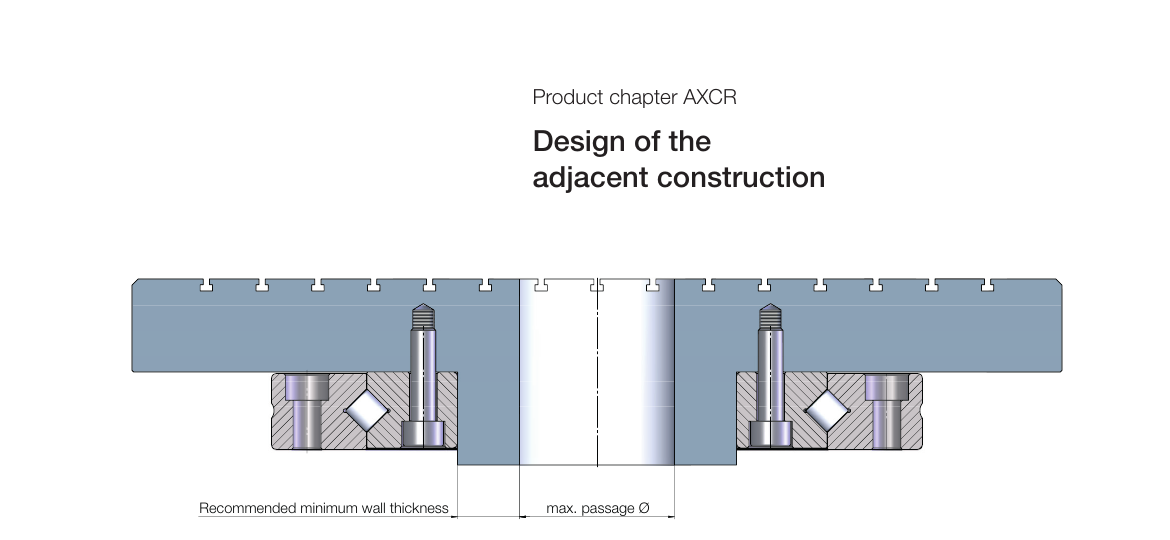
To ensure the housing does not deform due to bearing installation or load, sufficient wall thickness must be guaranteed. The following are the recommended minimum wall thicknesses and maximum through-hole diameters for each model:
AXCR-U Series
| Cross Roller Bearing | Minimum Wall Thickness [mm] | Maximum Through-hole Ø [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| AXCR 80-U | 15 | 50 |
| AXCR 90-U | 21 | 48 |
| AXCR 115-U | 22 | 71 |
| AXCR 160-U | 24 | 113 |
| AXCR 210-U | 30 | 150 |
| AXCR 270-U | 23 | 224 |
| AXCR 350-U | 34 | 283 |
| AXCR 360-U | 32 | 297 |
| AXCR 540-U | 31 | 478 |
AXCR-S Series
| Cross Roller Bearing | Minimum Wall Thickness [mm] | Maximum Through-hole Ø [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| AXCR 130-S | 13 | 104 |
| AXCR 150-S | 13 | 124 |
| AXCR 180-S | 13 | 154 |
| AXCR 220-S | 13 | 194 |
| AXCR 280-S | 13 | 254 |
| AXCR 360-S | 13 | 334 |
Design Principles
Wall Thickness Design
Ensure sufficient housing wall thickness to prevent deformation during installation and operation
Rigidity Design
Adjacent construction should have sufficient rigidity to support the loads transferred by the bearing
Heat Dissipation Consideration
Design should allow effective dissipation of heat generated by the bearing
Seal Protection
Consider adding additional sealing or dust protection measures
Mounting Hole Design
The mounting holes on the bearing rings should match the mounting holes in the adjacent construction.
Mounting Hole Notes
- Mounting hole positions should align with the holes on the bearing rings
- Screw specifications should meet recommended torque requirements
- Use correct screw torque; avoid over-tightening
- Tighten all screws evenly; diagonal sequence is recommended
Recommended Screw Torque
Screw torque according to DIN 912, strength class 10.9. For detailed torque values, please refer to the product dimension tables.
Design Recommendations
Best Practices
- Undersized, imprecise adjacent construction significantly reduces the rigidity at the bearing position
- On the other hand, structural support through additional components can also increase rigidity
- Consult the myonic application engineering team during the design phase
- Use FEA (Finite Element Analysis) to verify structural rigidity
- Consider the effect of temperature changes on fits
- Reserve sufficient space for maintenance and inspection