13.3 Technical Information and Alternative Versions
13.3.1 MINISLIDE MS Performance Parameters
| Maximum acceleration | 50 m/s² |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 1 m/s |
| Preload | Zero backlash |
| Accuracy | See sections 13.3.4 and 13.3.5 |
| Material - Guide rail, carriage, balls | Stainless steel, through-hardened steel |
| Material - Cage | POM |
| Temperature range | -40 °C to +80 °C (-40 °F to +176 °F) |
| Vacuum | Max. 10⁻⁷ mbar |
| Humidity | 10% – 70% (non-condensing) |
| Cleanroom | ISO 7 or ISO 6 class (per ISO 14644-1) |
13.3.2 MINISLIDE MSQ Performance Parameters
| Maximum acceleration | 300 m/s² |
|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 3 m/s |
| Preload | Zero backlash |
| Accuracy | See sections 13.3.4 and 13.3.5 |
| Material - Guide rail, carriage | Stainless steel, through-hardened steel |
| Material - Cage | PEEK |
| Material - Pinion | PEEK |
| Temperature range | -40 °C to +150 °C (-40 °F to +302 °F) |
| Vacuum | Max. 10⁻⁹ mbar |
| Humidity | 10% – 70% (non-condensing) |
| Cleanroom | ISO 7 or ISO 6 class (per ISO 14644-1) |
13.3.3 Reference Surfaces and Support Surfaces
The positioning and support surfaces of the carriage and guide rail are designated as follows:
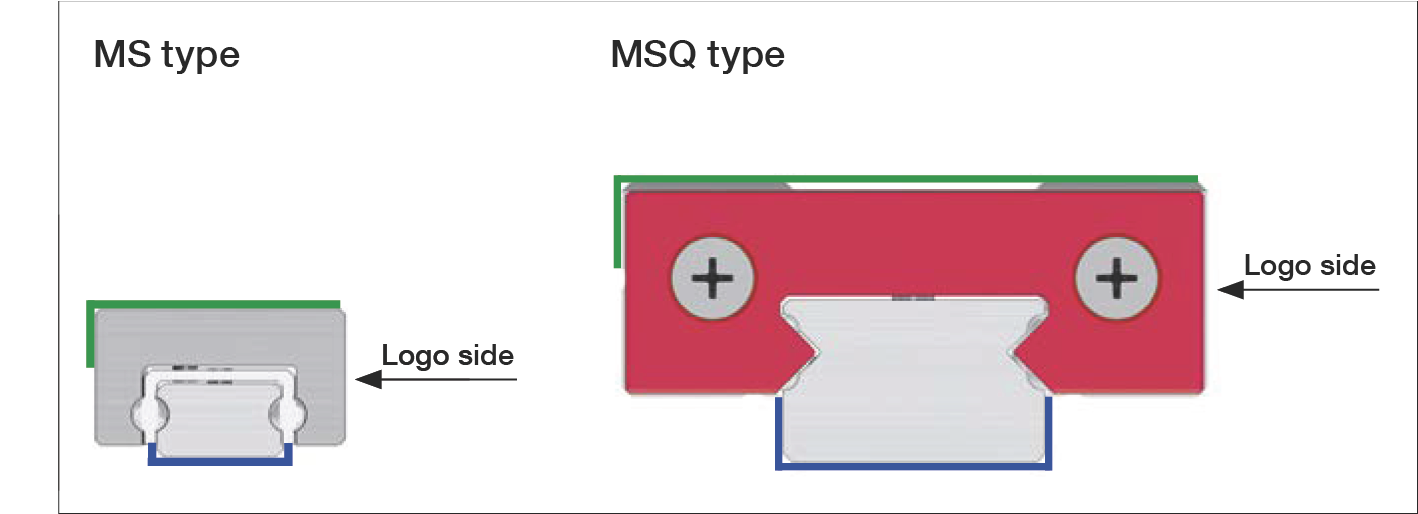
MS and MSQ type carriage positioning surfaces and guide rail positioning surfaces
Note: The reference surface of the carriage is located on the opposite side of the carriage from the company logo/model designation. The guide rail can be positioned on either side.
13.3.4 Running Accuracy and Support Surface Parallelism
The tolerance for stroke straightness depends on the length of the guide rail. The table below shows the corresponding maximum values.
Measurements are taken in an unloaded state on a flat surface.
Stroke Straightness (Horizontal and Vertical)
| System length L | Straightness |
|---|---|
| 10 – 30 mm | 3 μm |
| 40 – 80 mm | 4 μm |
| 90 – 130 mm | 5 μm |
Support Surface Parallelism (Friction-free Table at Center Position)
| System length L | Parallelism |
|---|---|
| 10 – 30 mm | 12 μm |
| 40 – 80 mm | 15 μm |
| 90 – 130 mm | 18 μm |
13.3.5 Total Height Tolerance
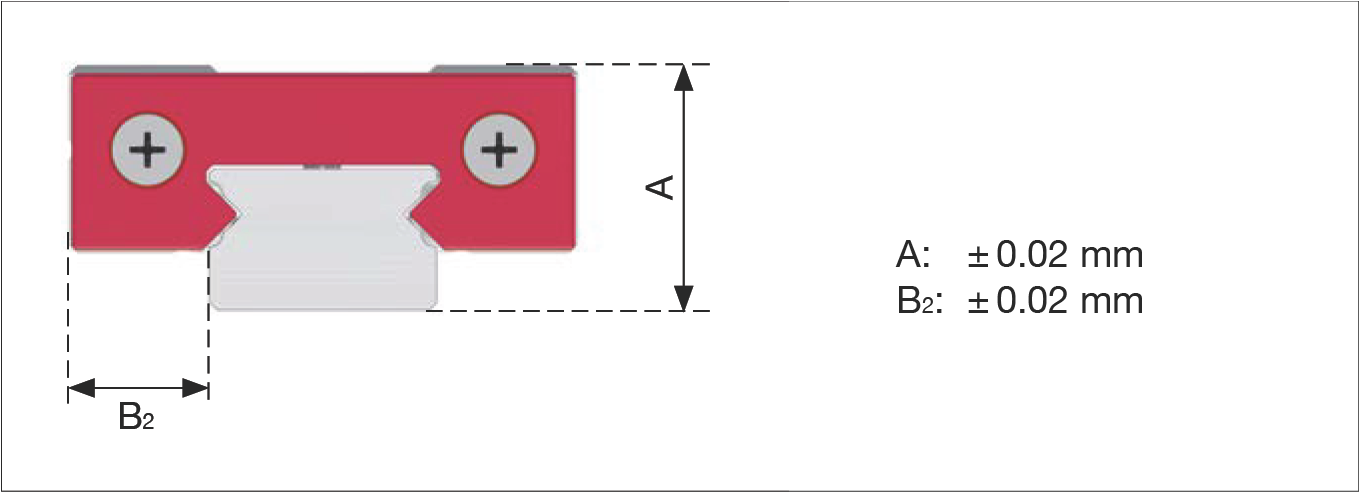
A: ± 0.02 mm, B2: ± 0.02 mm
13.3.6 Push Force and Preload
Push force is affected by preload and the lubricant used. MINISLIDE guideways are delivered as standard with zero backlash and light preload.
Upon request, carriages can be delivered with a defined push force (see section 14.1).
13.3.7 Friction and Smoothness
SCHNEEBERGER attaches great importance to smoothness during the manufacturing process. The accuracy of surfaces and materials has the highest priority. This also applies to the rolling elements used, which must meet the strictest quality requirements. Under normal operating conditions, a friction coefficient of 0.003 can be assumed.
13.3.8 Dimension Tables, Load Capacity, Weight and Moment Loads
The following provides detailed dimension tables, load capacity, weight and moment load information for various MINISLIDE models.
MS 4
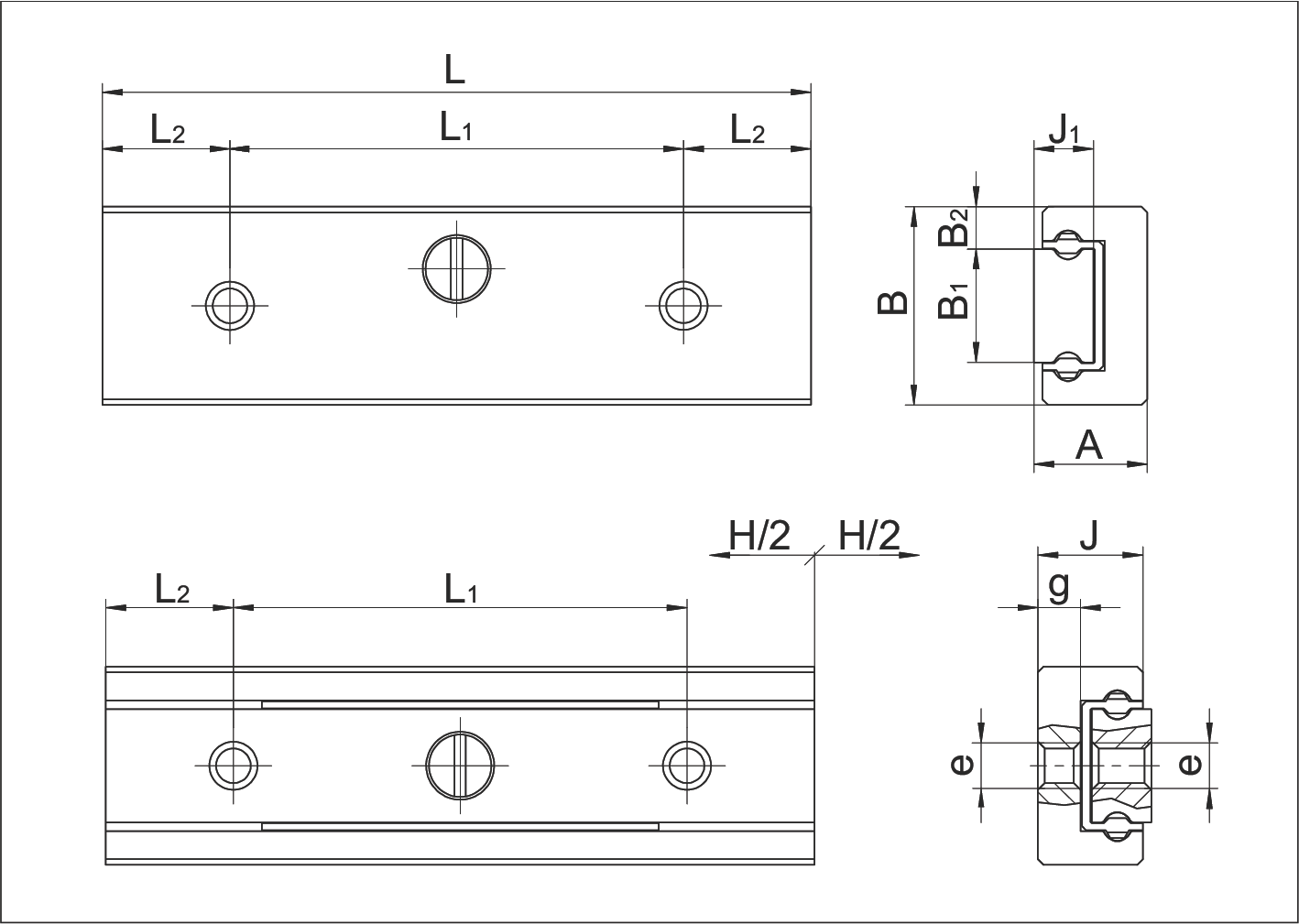
MS 4 Dimension Drawing
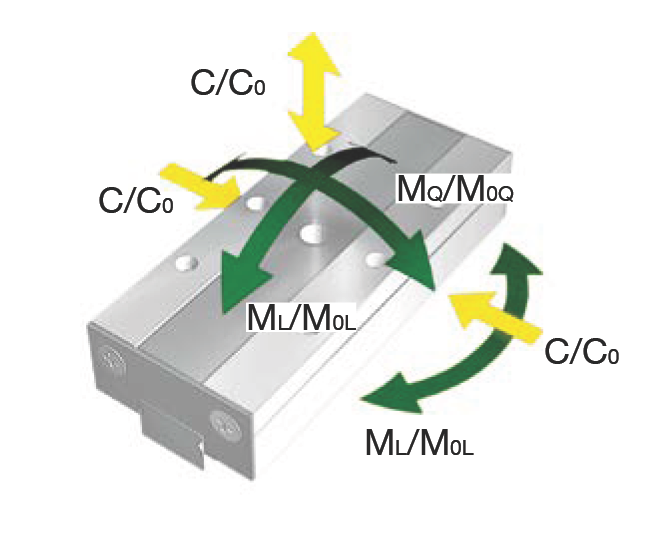
Load and Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification Item | MS 4-10.6 | MS 4-15.12 | MS 4-20.15 | MS 4-25.22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| A | System height | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| B | System width | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| B1 | Rail width | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| J | Carriage height | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| J1 | Rail height | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| H | Stroke | 6 | 12 | 15 | 22 |
| L | System length | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 5 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 2.5 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 |
| e | Thread | M1.6 | M1.6 | M1.6 | M1.6 |
| g | Available thread length | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Ball diameter | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Load Capacity (N) | |||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 277 | 347 | 485 | 555 |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 207 | 242 | 307 | 337 |
| Torque (Nm) | |||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 0.60 | 0.75 | 1.04 | 1.19 |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 0.40 | 0.61 | 1.13 | 1.46 |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.66 | 0.72 |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| Weight (g) | |||||
| Weight | 1.7 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 4.3 | |
MS 5
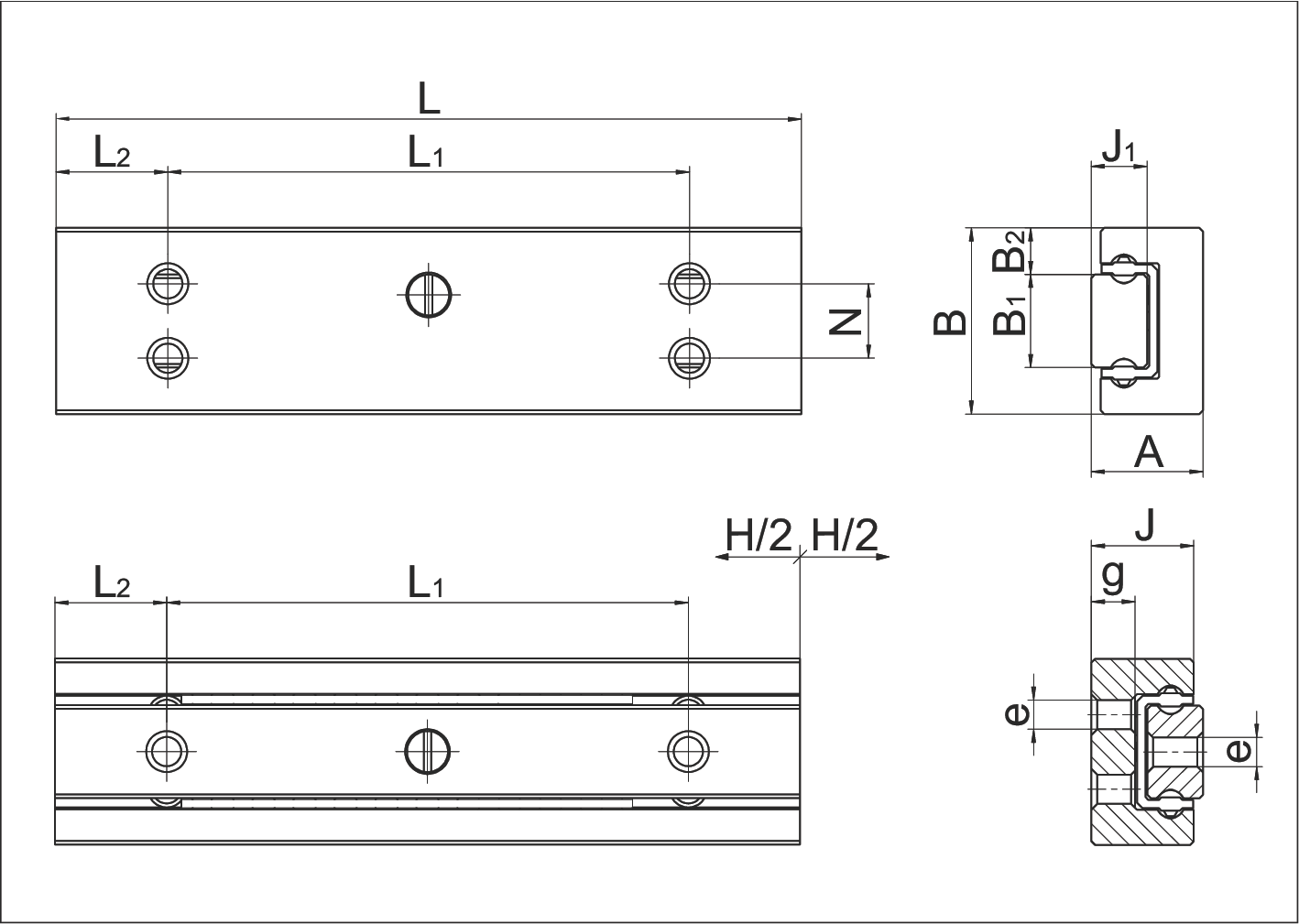
MS 5 Dimension Drawing
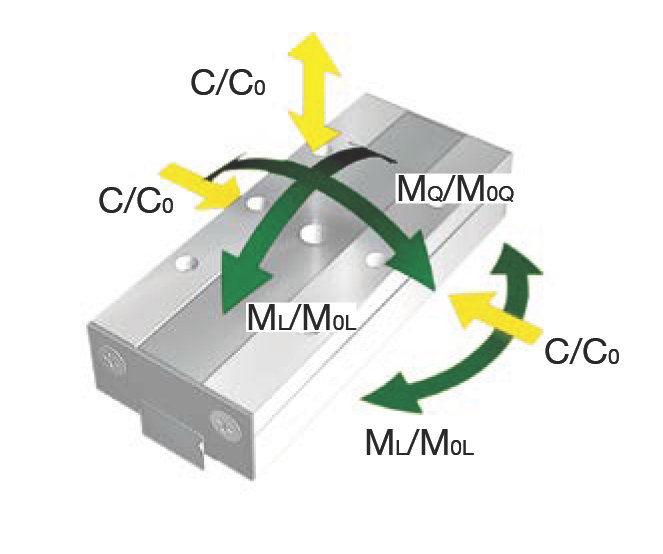
Load and Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification Item | MS 5-15.8 | MS 5-20.13 | MS 5-30.20 | MS 5-40.31 | MS 5-50.42 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | ||||||
| A | System height | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| B | System width | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| B1 | Rail width | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| J | Carriage height | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| J1 | Rail height | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| H | Stroke | 8 | 13 | 20 | 31 | 42 |
| L | System length | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 8 | 12 | 20 | 28 | 36 |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 3.5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| N | Lateral mounting hole spacing | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| e | Thread | M2 | M2 | M2 | M2 | M2 |
| g | Available thread length | 2.35 | 2.35 | 2.35 | 2.35 | 2.35 |
| Ball diameter | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Load Capacity (N) | ||||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 780 | 936 | 1404 | 1716 | 2028 |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 568 | 645 | 857 | 987 | 1109 |
| Torque (Nm) | ||||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 2.18 | 2.62 | 3.93 | 4.80 | 5.68 |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 1.72 | 2.4 | 5.15 | 7.55 | 10.4 |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 1.59 | 1.81 | 2.40 | 2.76 | 3.11 |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 1.25 | 1.66 | 3.14 | 4.34 | 5.69 |
| Weight (g) | ||||||
| Weight | 5.4 | 7.3 | 11 | 14.8 | 18.6 | |
MSQ 7
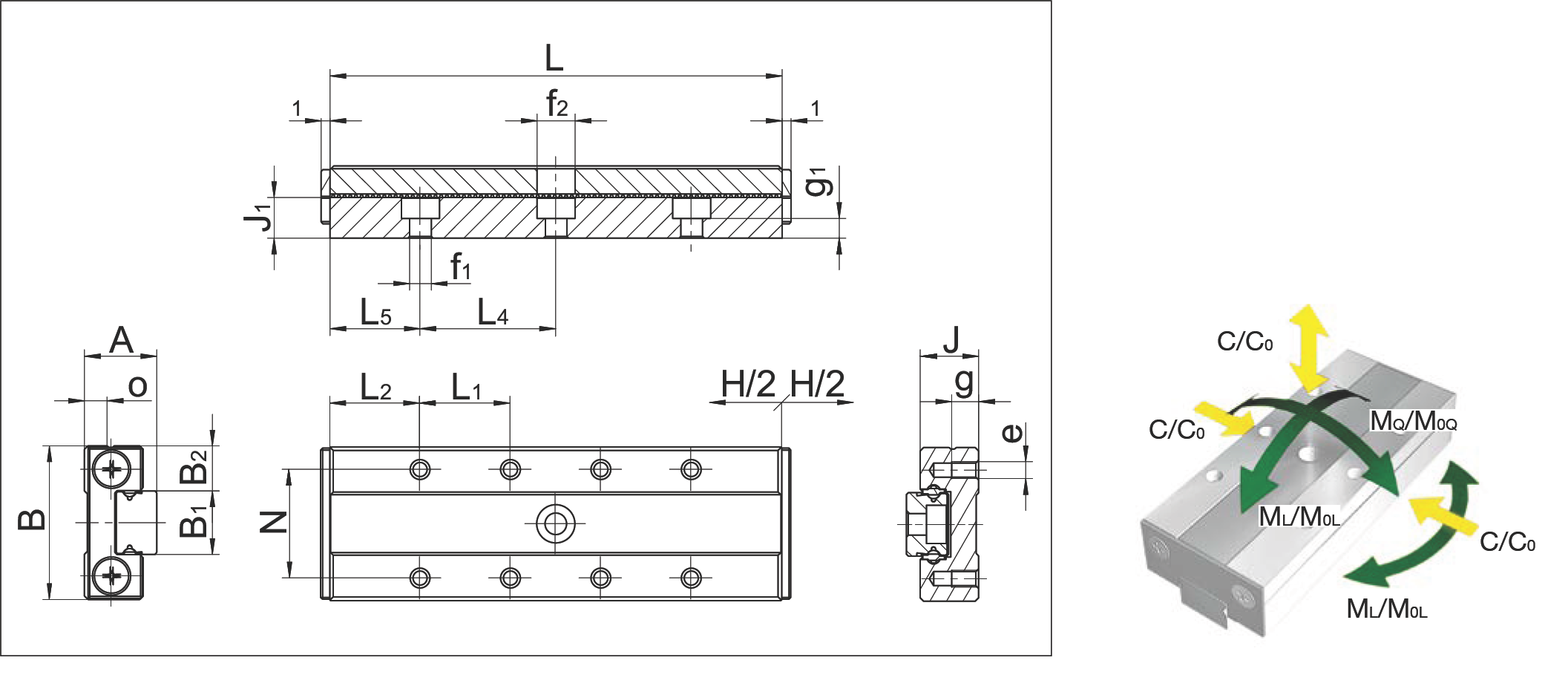
MSQ 7 Dimension Drawing and Load Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification Item | MSQ 7-30.20 | MSQ 7-40.28 | MSQ 7-50.36 | MSQ 7-60.50 | MSQ 7-70.58 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | ||||||
| A | System height | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| B | System width | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| B1 | Rail width | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| J | Carriage height | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| J1 | Rail height | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| H | Stroke | 20 | 28 | 36 | 50 | 58 |
| L | System length | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| L4 | Mounting hole spacing | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| L5 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 7.5 | 5 | 10 | 7.5 | 5 |
| N | Lateral mounting hole spacing | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| e | Thread | M2 | M2 | M2 | M2 | M2 |
| f1 | Mounting hole diameter | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| f2 | Screw hole diameter | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| g | Available thread length | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| g1 | Clamping length | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| Ball diameter | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Load Capacity (N) | ||||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 1193 | 1670 | 2148 | 2386 | 2864 |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 609 | 770 | 919 | 989 | 1124 |
| Torque (Nm) | ||||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 5.1 | 7.2 | 9.2 | 10.3 | 12.3 |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 5.0 | 8.6 | 13.1 | 15.8 | 21.8 |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 2.6 | 3.3 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.8 |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 2.5 | 4.0 | 5.6 | 6.5 | 8.5 |
| Weight (g) | ||||||
| Weight | 24.5 | 32.6 | 40.5 | 48.5 | 56.3 | |
MSQ 9
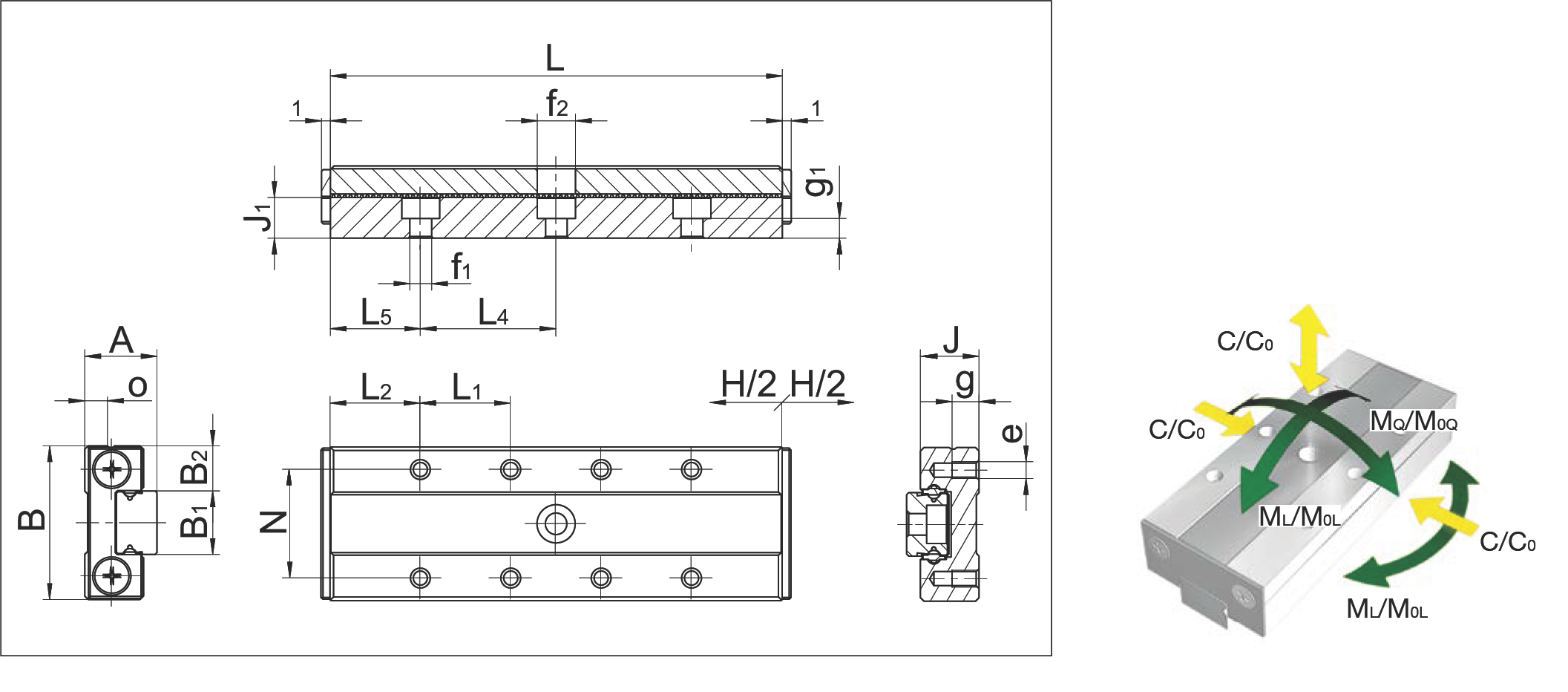
MSQ 9 Dimension Drawing and Load Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification Item | MSQ 9-40.34 | MSQ 9-50.42 | MSQ 9-60.50 | MSQ 9-70.58 | MSQ 9-80.66 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | ||||||
| A | System height | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| B | System width | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| B1 | Rail width | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| J | Carriage height | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| J1 | Rail height | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| H | Stroke | 34 | 42 | 50 | 58 | 66 |
| L | System length | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| L4 | Mounting hole spacing | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| L5 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 10 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 10 |
| N | Lateral mounting hole spacing | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| e | Thread | M3 | M3 | M3 | M3 | M3 |
| f1 | Mounting hole diameter | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| f2 | Screw hole diameter | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| g | Available thread length | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| g1 | Clamping length | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Ball diameter | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Load Capacity (N) | ||||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 1432 | 1909 | 2386 | 2864 | 3341 |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 692 | 846 | 989 | 1124 | 1252 |
| Torque (Nm) | ||||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 7.6 | 10.1 | 12.6 | 15.2 | 17.7 |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 6.7 | 10.8 | 15.8 | 21.8 | 28.7 |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 3.7 | 4.5 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 6.6 |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 3.2 | 4.8 | 6.5 | 8.5 | 10.7 |
| Weight (g) | ||||||
| Weight | 45.6 | 56.9 | 68.1 | 79.2 | 90.3 | |
MSQ 12
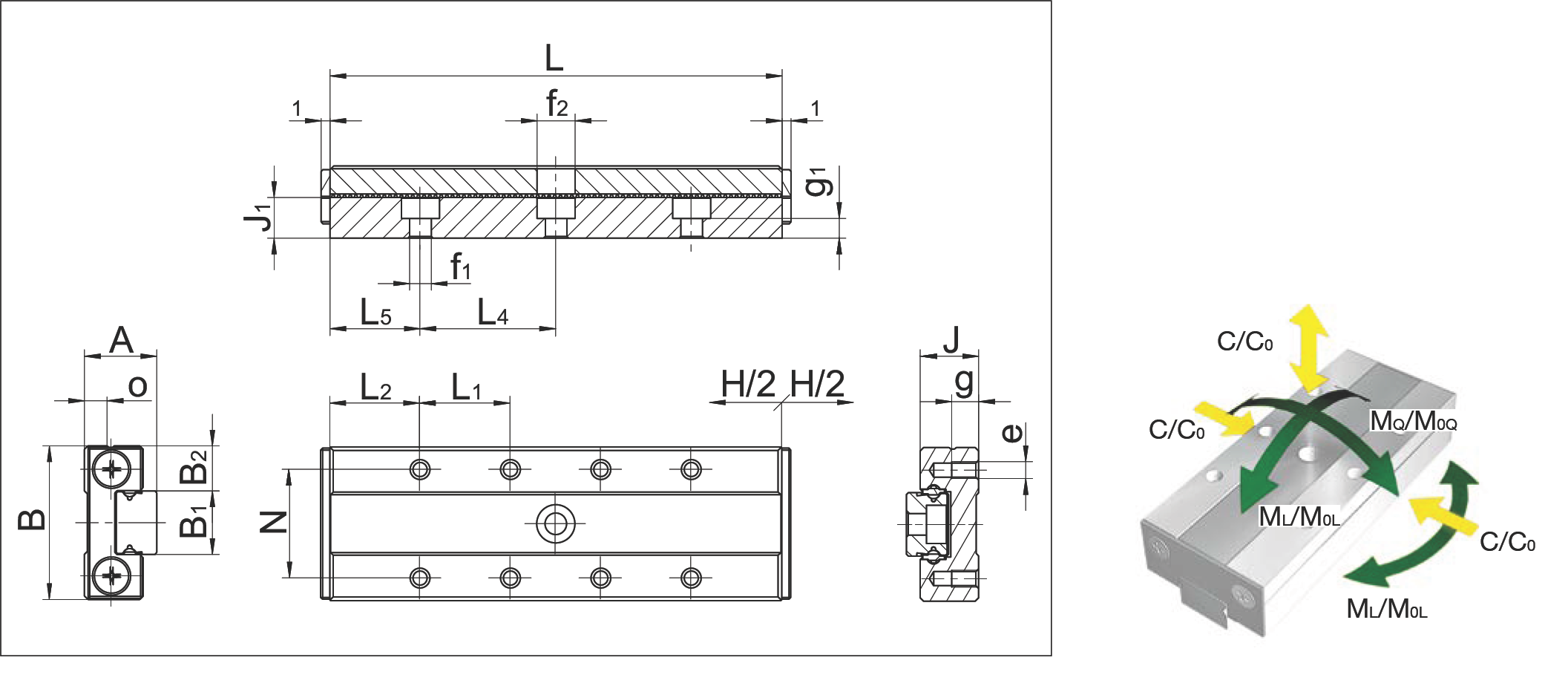
MSQ 12 Dimension Drawing and Load Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification Item | MSQ 12-50.45 | MSQ 12-60.48 | MSQ 12-80.63 | MSQ 12-100.70 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| A | System height | 13 | 13 | 13 | 13 |
| B | System width | 27 | 27 | 27 | 27 |
| B1 | Rail width | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| J | Carriage height | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| J1 | Rail height | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
| H | Stroke | 45 | 48 | 63 | 70 |
| L | System length | 50 | 60 | 80 | 100 |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 10 | 7.5 | 10 | 12.5 |
| L4 | Mounting hole spacing | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| L5 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 12.5 | 5 | 15 | 12.5 |
| N | Lateral mounting hole spacing | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| e | Thread | M3 | M3 | M3 | M3 |
| f1 | Mounting hole diameter | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| f2 | Screw hole diameter | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| g | Available thread length | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| g1 | Clamping length | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Ball diameter | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Load Capacity (N) | |||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 2685 | 3759 | 5370 | 7518 |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 1427 | 1806 | 2318 | 2934 |
| Torque (Nm) | |||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 18.9 | 26.5 | 37.9 | 53.0 |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 15.7 | 27.0 | 49.5 | 90.1 |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 10.1 | 12.7 | 16.3 | 20.7 |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 8.3 | 12.9 | 21.4 | 35.1 |
| Weight (g) | |||||
| Weight | 103.9 | 124.4 | 165.5 | 206.5 | |
MSQ 15
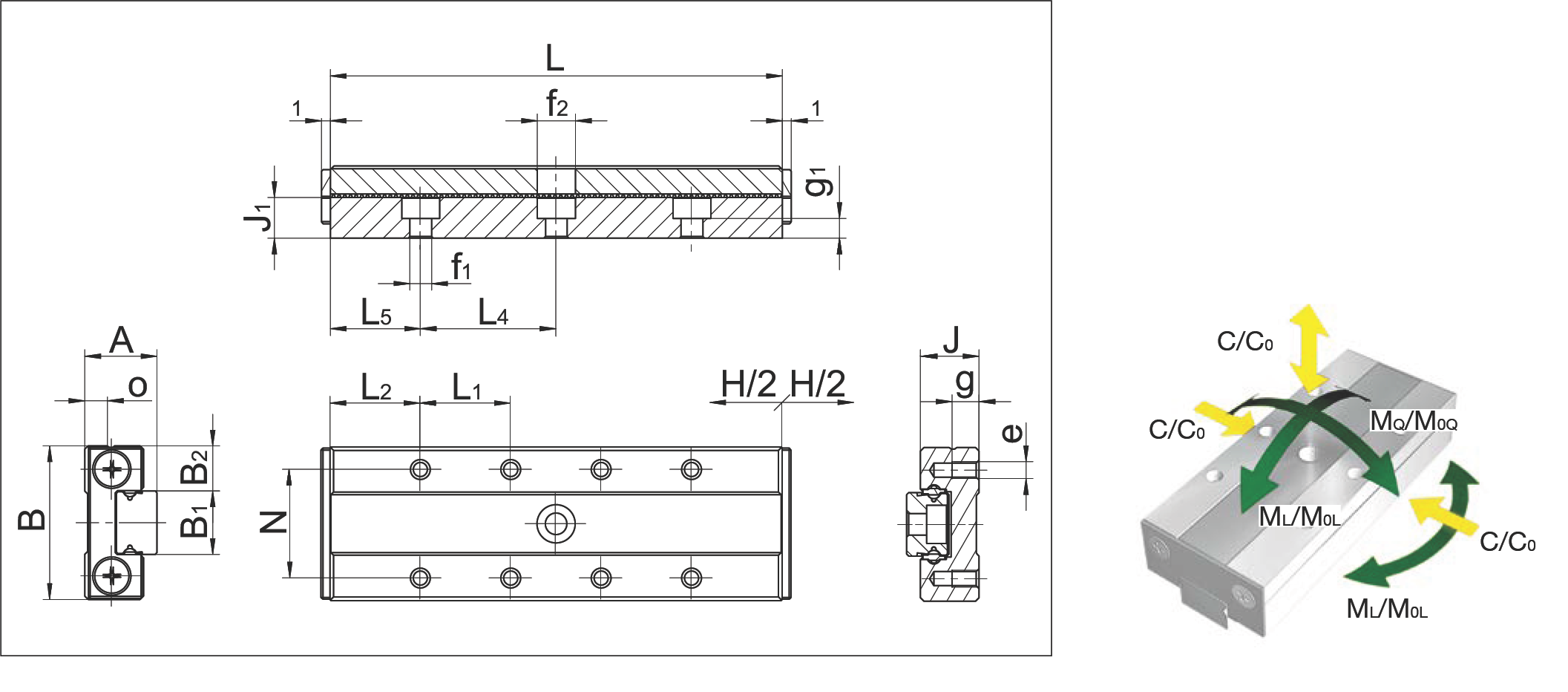
MSQ 15 Dimension Drawing and Load Moment Direction Diagram
| Specification | MSQ 15-70.66 | MSQ 15-90.70 | MSQ 15-110.96 | MSQ 15-130.102 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | ||||||
| A | System height | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | |
| B | System width | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | |
| B1 | Rail width | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| B2 | Distance between positioning surfaces | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.5 | |
| J | Carriage height | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | |
| J1 | Rail height | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | |
| H | Stroke | 66 | 70 | 96 | 102 | |
| L | System length | 70 | 90 | 110 | 130 | |
| L1 | Mounting hole spacing | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| L2 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | |
| L4 | Mounting hole spacing | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | |
| L5 | Mounting hole start/end spacing | 15 | 5 | 15 | 5 | |
| N | Lateral mounting hole spacing | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| e | Thread | M3 | M3 | M3 | M3 | |
| f1 | Mounting hole diameter | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | |
| f2 | Screw hole diameter | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| g | Available thread length | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| g1 | Clamping length | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Ball diameter | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Load Capacity (N) | ||||||
| C₀ | Static load capacity | 4773 | 7637 | 8592 | 11456 | |
| C | Dynamic load capacity (≙ C₁₀₀) | 2611 | 3628 | 3940 | 4820 | |
| Torque (Nm) | ||||||
| M₀Q | Permissible lateral static torque | 42.5 | 68 | 76.5 | 102.0 | |
| M₀L | Permissible longitudinal static torque | 36.7 | 80.9 | 99.5 | 166.6 | |
| MQ | Permissible lateral dynamic torque | 23.2 | 32.3 | 35.1 | 42.9 | |
| ML | Permissible longitudinal dynamic torque | 20.1 | 38.4 | 45.6 | 70.1 | |
| Weight (g) | ||||||
| 216.2 | 277.5 | 338.6 | 399.5 | |||
13.3.9 Lubrication
Lubrication is a design element and must therefore be defined during the development phase of the machine or application. If lubrication is only selected after design and construction are complete, according to our experience, this can lead to considerable performance difficulties. Therefore, a well-thought-out lubrication concept is a sign of state-of-the-art and well-designed equipment.
Parameters to consider when selecting a lubricant include:
- Operating conditions (speed, acceleration, stroke, load, installation orientation)
- External influences (temperature, corrosive media or radiation, contamination, humidity, vacuum, cleanroom)
- Subsequent lubrication (cycle time, quantity)
- Compatibility (with other lubricants, corrosion protection and integrated materials such as plastics)
Technical and economic considerations determine the lubricant used.
MINISLIDE Initial Lubrication
MINISLIDE products are lubricated at the factory with Klübersynth GE 46-1200.
MINISLIDE Subsequent Lubrication Intervals
Lubricant should be applied to the guide rail. Subsequent lubrication intervals depend on various influencing variables such as load, working environment, speed, etc., and therefore cannot be calculated. The lubrication area should therefore be monitored over an extended period.
A) Subsequent Lubrication with Oil
For subsequent lubrication with oil, mineral oil CLP (DIN 51517) or HLP (DIN 51524) with a viscosity range between ISO VG32 and ISO VG150, in accordance with DIN 51519, is recommended. During lubrication, the carriage/guide rail should be moved along the entire stroke length to properly distribute the lubricant.
B) Subsequent Lubrication with Grease
For lubrication with grease, grease KP2K or KP1K according to DIN 51825 is recommended. During lubrication, the carriage/guide rail should be moved along the entire stroke length to properly distribute the lubricant.
Custom Lubricants
Special lubricants are used for specific purposes. For example, lubricants for vacuum, cleanroom, high or low temperatures, high speeds or high stroke frequencies. SCHNEEBERGER can supply guideways with the appropriate lubricant for any of these application areas (see section 14.2).