5.1.1 Features and Advantages
The SCHNEEBERGER rack and pinion MONORAIL BZ system combines the characteristic performance of SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL BM guide rails with the advantages of high-precision integral rack drives.
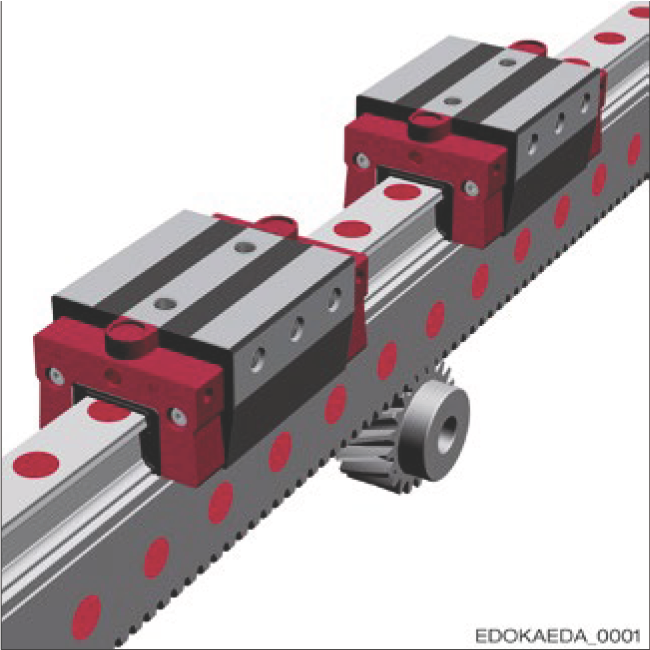

Dual Carriage Rack Drive
The system offers customers the following advantages:
- One-piece system lengths up to 6,000 mm
- Multi-segment systems > 6,000 mm
- High-quality racks (hardened and ground)
- Cost savings of up to 25% due to reduced indirect costs for design, manufacturing, and installation
- Excellent running characteristics, high load capacity, and extended service life based on SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL BM guide rails
- Meeting customer requirements through a wide range of carriage types, extensive accessories, and racks of different quality grades
Additionally, MONORAIL BZ features:
- Butt joint capability due to its specially developed transition geometry
- Combining guiding, driving, and measuring functions in a single system
- Transmission of high lateral forces
- Double the number of fixing screws between system and base structure, and between rack and guide rail
- Considerable system height with more favorable lever ratios
- Reduced handling and installation expenses as transport fixtures can be used for system installation
- Interchangeability of individual rack segments (e.g., in heavily worn sections)
One-Piece System Lengths Up to 6,000 mm
Using one-piece system lengths of up to 6,000 mm, precise, backlash-free carriage operation over large distances is achieved. By connecting multiple BZ systems together, even greater travel distances can be achieved while ensuring consistent quality.
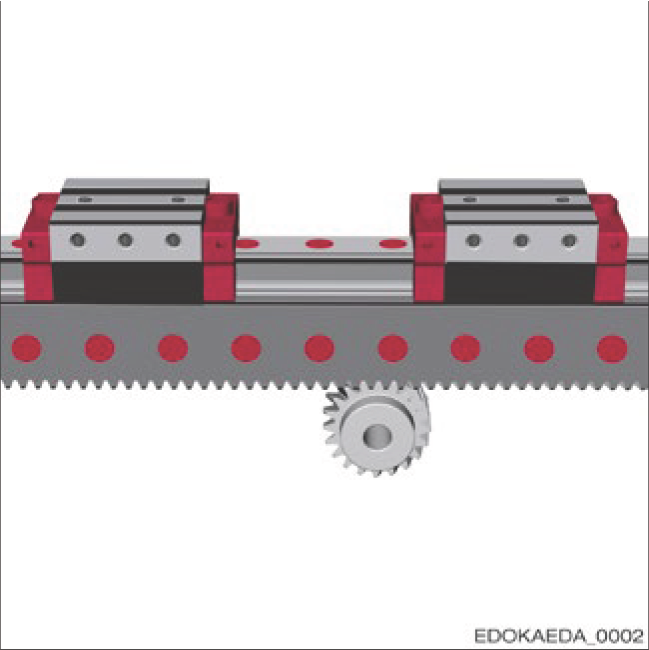
BZ System with Rack Drive
Quality Grade 6 Gear Machining
Ground and hardened quality grade 6 racks support precise operation with maximum force transmission, high positioning accuracy, and extended service life. Other quality grades and designs are available.
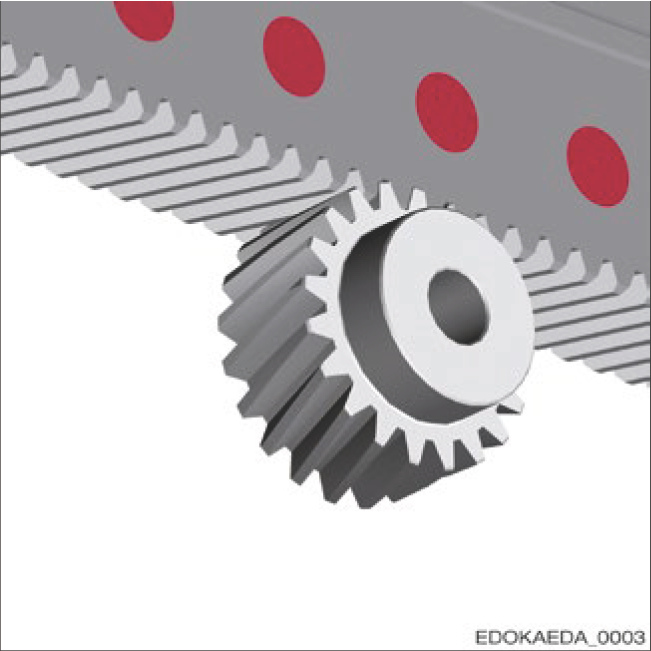
Rack and Pinion
5.1.2 Installation Direction
The installation direction of the guide rail is based on the application, i.e., based on the function of the machine, its structure, and the travel direction of the axis. It affects the lubricant supply method and the contamination sensitivity of the guide rail. The following illustrations explain this machine concept:
| Variant | Description |
|---|---|
| Variant 1* | 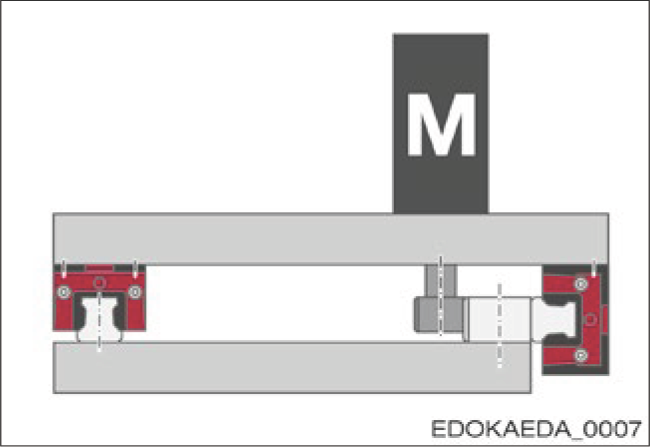 Features:
|
| Variant 2* | 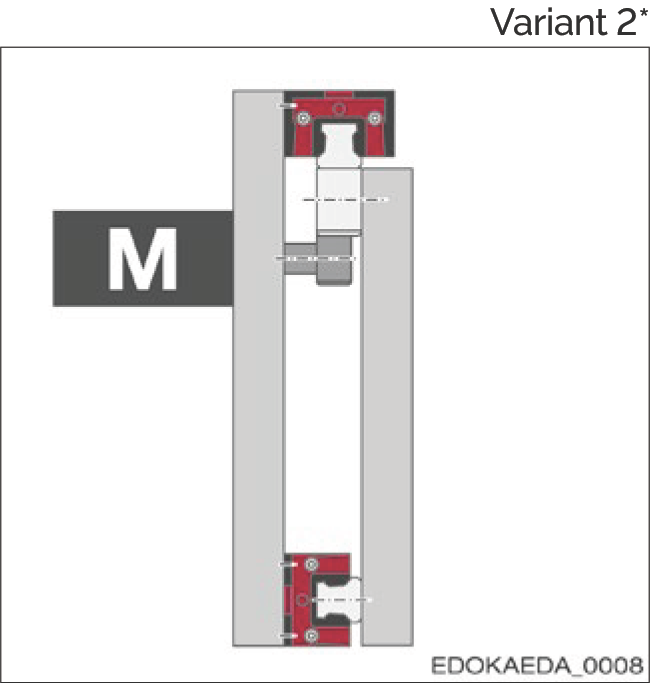 Features:
The locating surfaces of both guide rails and carriages are at the same level Note: * M = Motor with gear and pinion |
| Variant 3* | 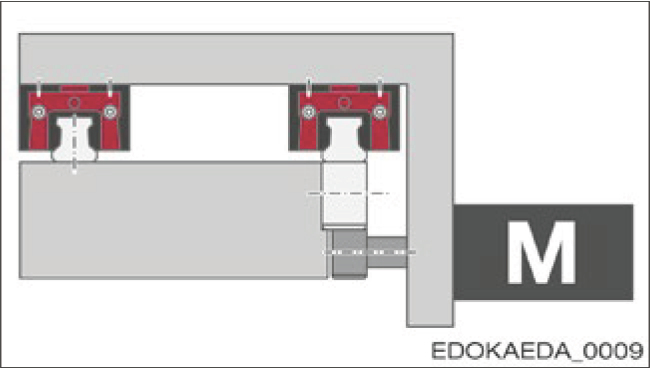 Features:
Note: * M = Motor with gear and pinion |
| Variant 4* | 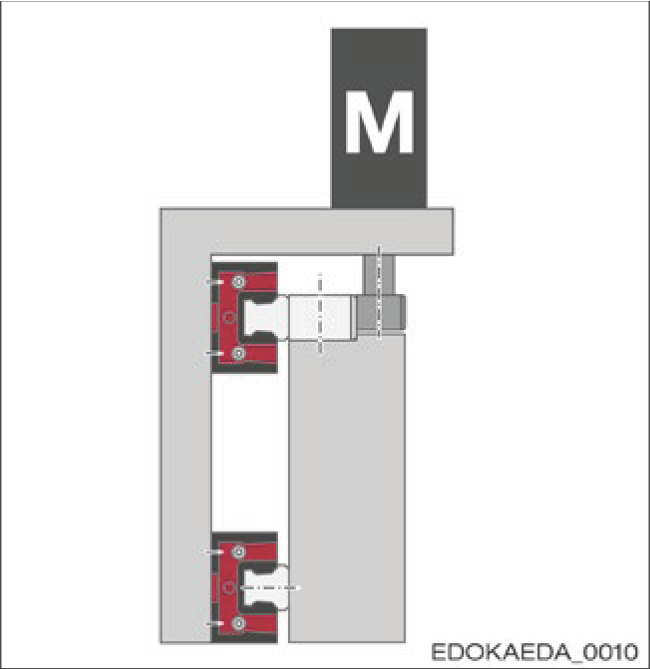 Features:
Note: * M = Motor with gear and pinion |