Different application areas require different characteristics of linear guideways and recirculating units.
Various parameters and factors must be considered when selecting products. The following explains these key considerations in detail.
Relationship Between Stroke H and Length of the Guideway L
If the Stroke is Below 400 mm
If the Stroke is Above 400 mm
| L | = Length of the linear guideway in mm |
| H | = Possible Stroke in mm |
Calculating the Cage Length K
If the Stroke is Symmetrical
If the Stroke is Asymmetrical
H > H₁ + H₂
H₁₂ = H₁ + H₂
| K | = Cage length in mm |
| L | = Length of the linear guideway in mm |
| H | = Possible Stroke in mm |
| H₁ | = Large partial stroke in mm = H/2 |
| H₂ | = Small partial stroke in mm = H/2 |
| H₁₂ | = Effective partial stroke in mm |
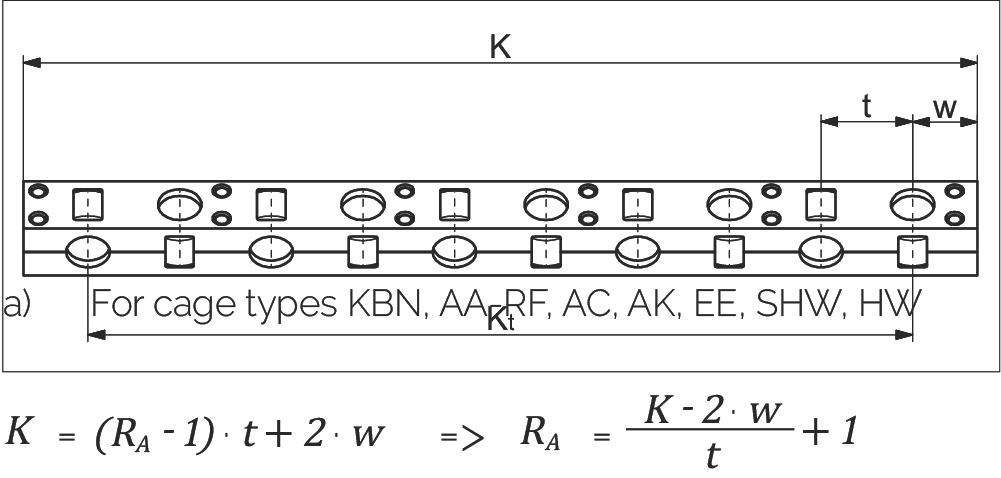
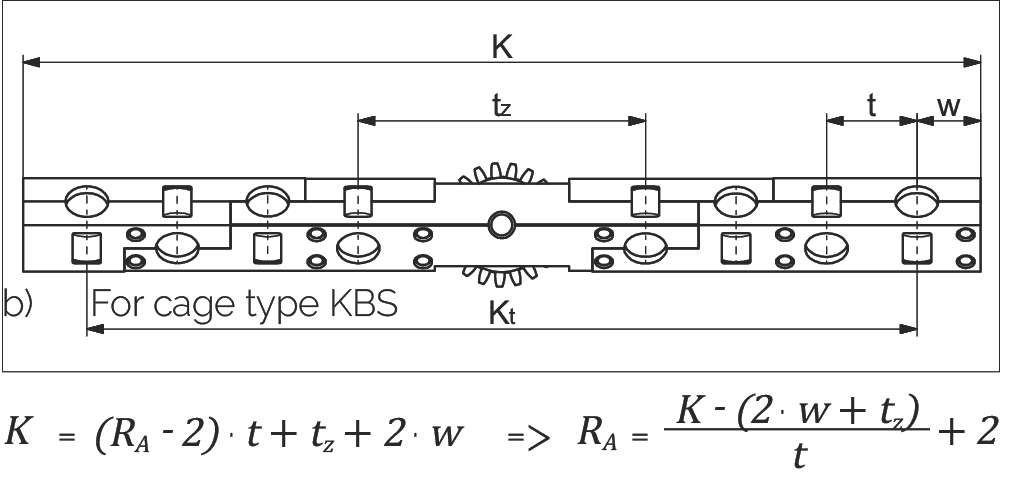
Calculating the Number of Rolling Elements (RA) per Cage
a) For Cage Types KBN, AA-RF, AC, AK, EE, SHW, HW
or
b) For Cage Type KBS
or
| K | = Cage length in mm | t | = Cage division in mm |
| RA | = Total available rolling elements per cage | Kt | = Load-bearing length in mm |
| w | = Distance from cage start to the middle of the first rolling element in mm | tz | = Length of the middle section for the KBS cage |
Relationship Between Cage Length K and Average Guideway Spacing Q
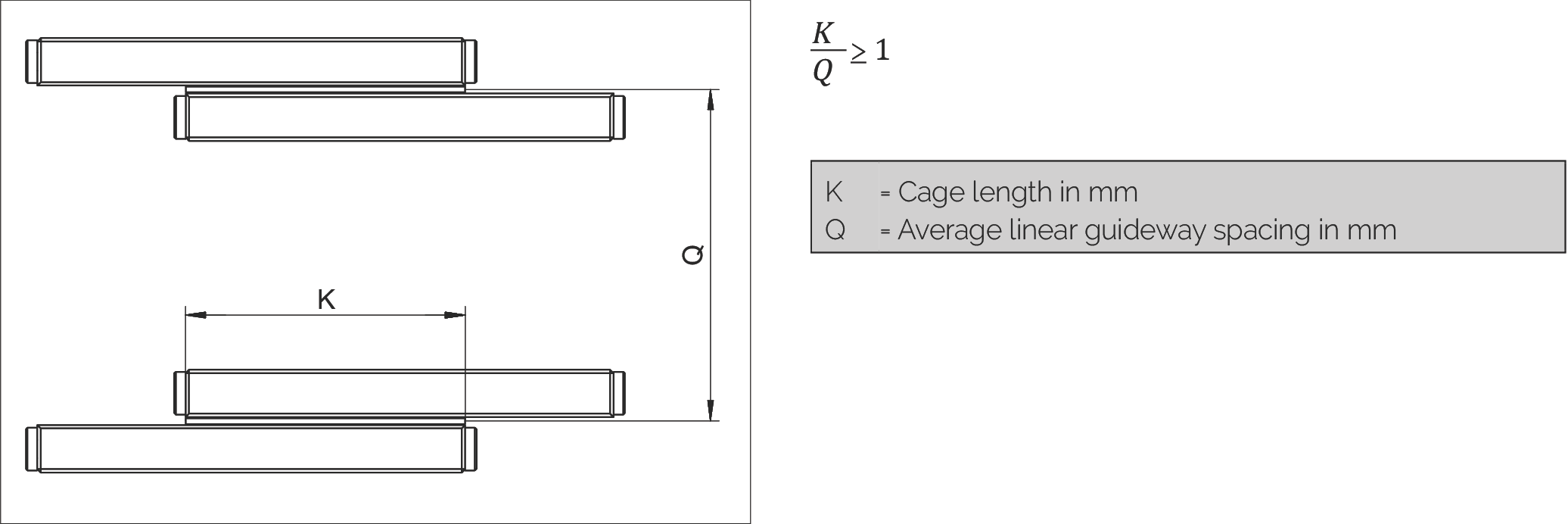
| K | = Cage length in mm |
| Q | = Average linear guideway spacing in mm |
Maximum Permissible Installation Ratio for Overrunning Cages
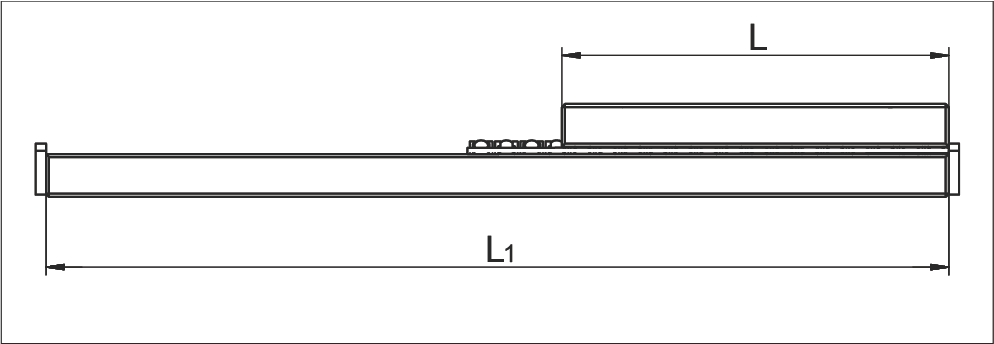
Overrunning cages are an effective solution when a short table needs to be moved on a long guideway track. In this case, the short tracks of the guideway must be equipped with rounded run-ins (special version EG, see chapter 7.3) to minimize the pulsation caused by the overrunning cage.
Maximum Permitted Installation Ratios L to L₁:
| For fixed guideways | 1 : 2 |
| For laid on guideways | 1 : 4 |
Installation Variants for Linear Guideways
There are four installation variants for linear guideways. Various linear guideways can also use wipers in the form of end pieces (a₁)*. In all four cases, the following length ratios apply:
Variant 1
- Equal length tracks
- Symmetrical/asymmetrical stroke
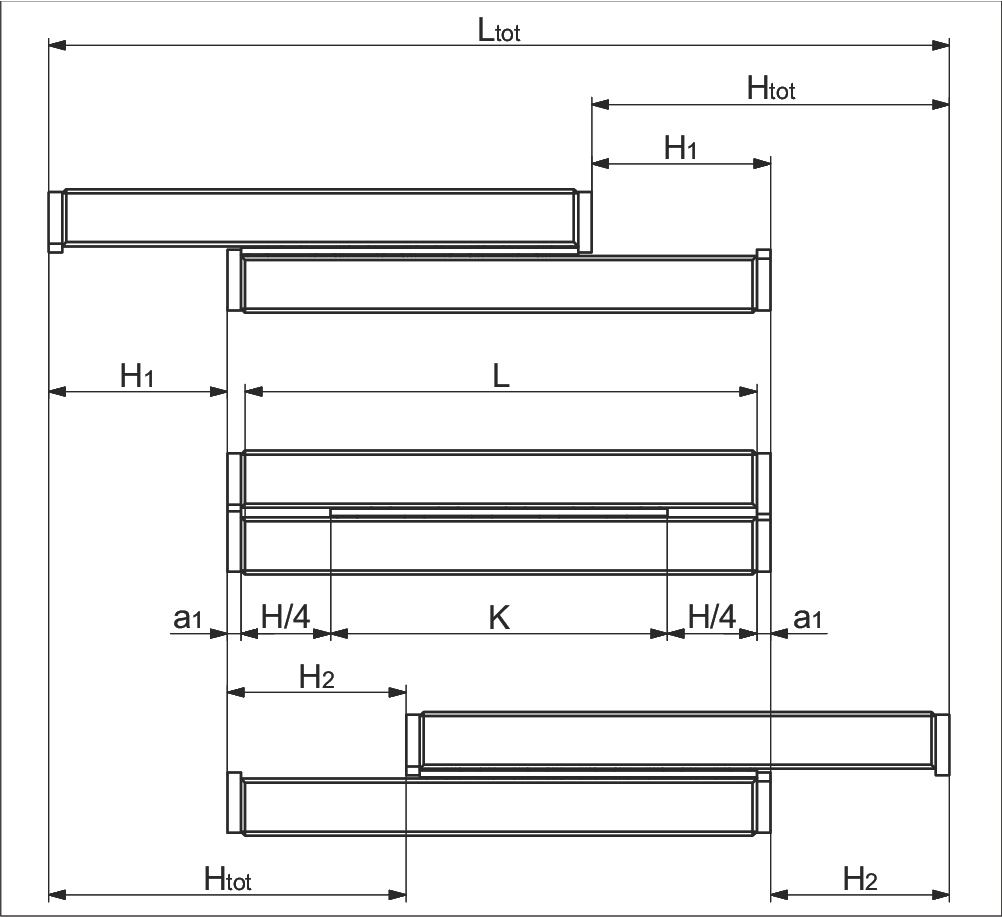
a) Without end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers
b) For end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers**
Variant 2
- Equal length tracks
- Unidirectional stroke
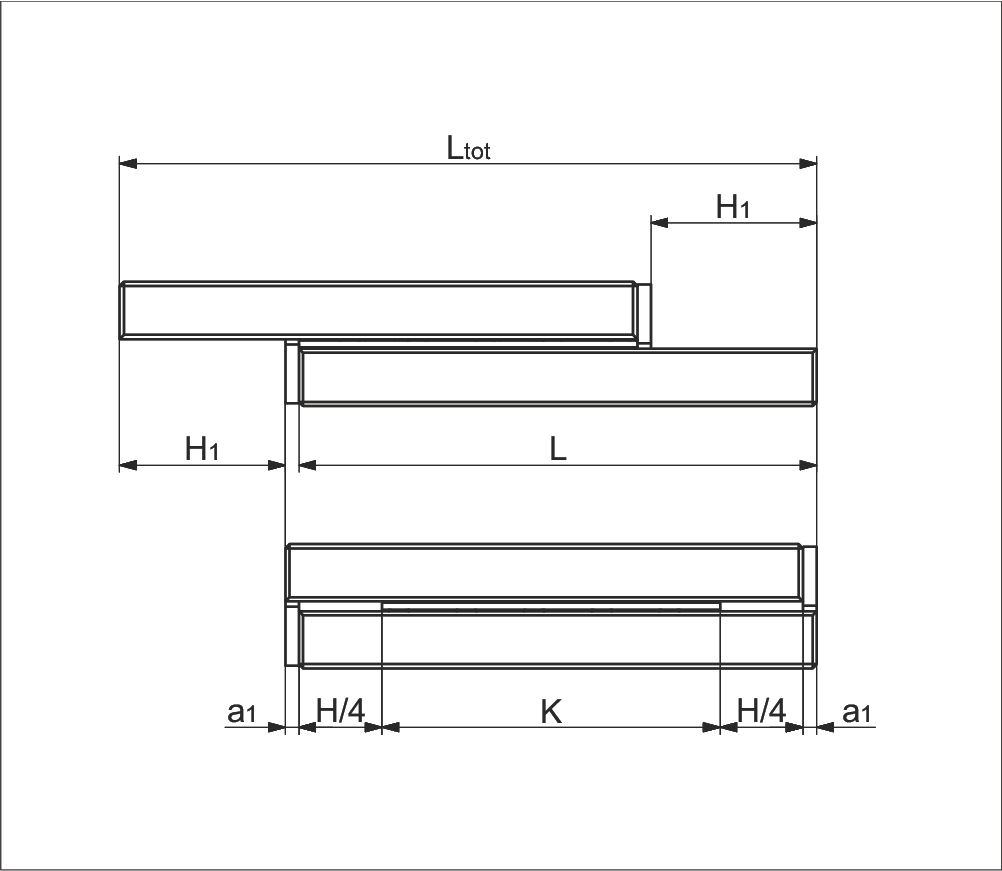
a) Without end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers
b) For end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers**
Variant 3
- Unequal length tracks
- Symmetrical/asymmetrical stroke
- Short track additional
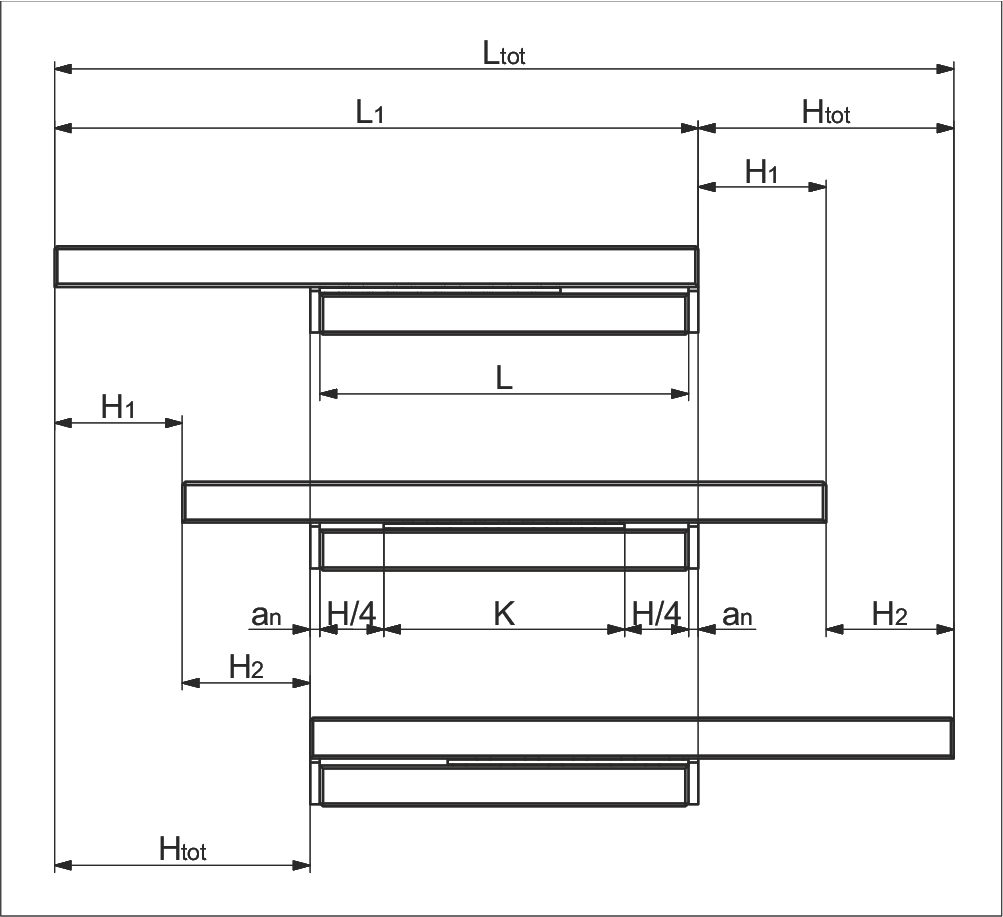
a) Without end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers
b) For end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers**
Variant 4
- Unequal length tracks
- Symmetrical/asymmetrical stroke
- Long track additional
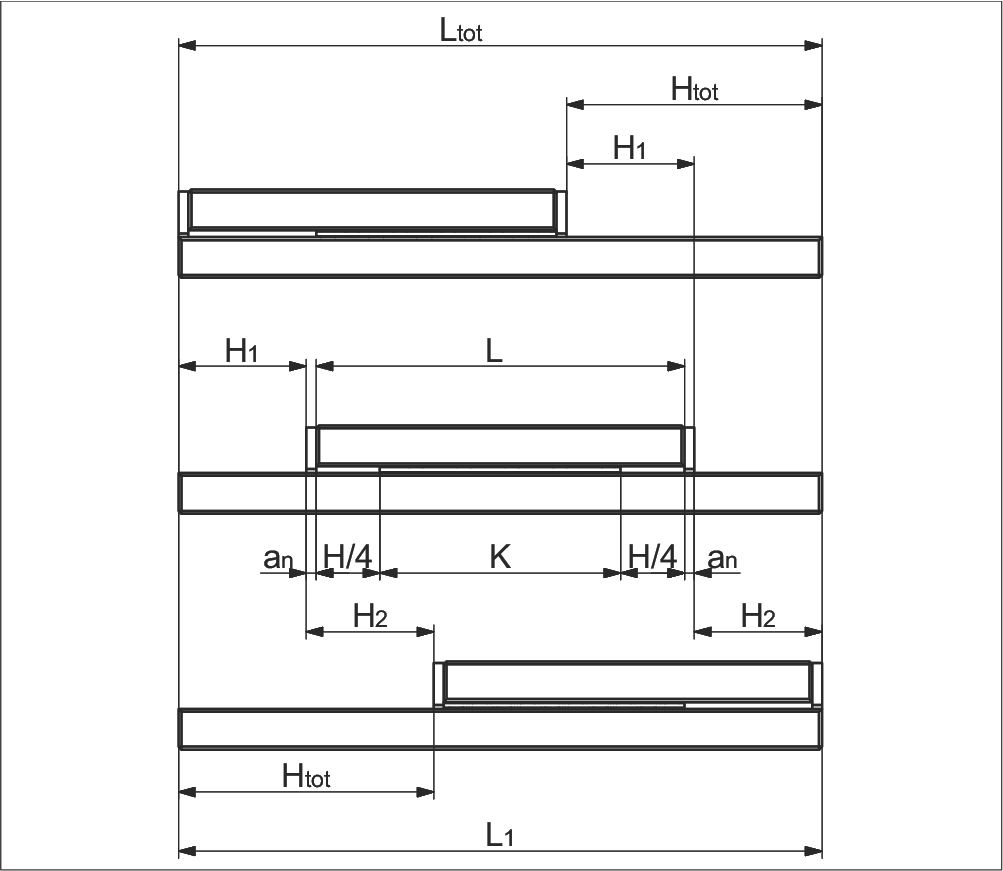
a) Without end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers
b) For end screws, end pieces, and end pieces with wipers**
Parameter Explanation
| K | = Cage length in mm | H | = Possible stroke in mm |
| H₁ | = Large partial stroke in mm = H/2 | H₂ | = Small partial stroke in mm ≤ H/2 |
| Htot | = Effective partial stroke in mm | H12 | = Total partial stroke in mm = H1 + H2 |
| L | = Length in mm | L₁ | = Long track length in mm |
| Ltot | = Total length in mm | an | = Thickness of the end piece in mm |
* a₁ End screws, end pieces and end pieces with wipers, see chapter 5
** Wipers may affect the running characteristics of the linear guideway