1.7.1 Terminology Definitions
The service life of profiled rail guideways is characterized by the travel distance, i.e., the distance that can be traveled under specified load before initial fatigue symptoms appear. Service life calculation is an important basis for selecting the appropriate guideway size.
According to DIN ISO 14728-1, the nominal service life can be calculated using the following formula:

Nominal service life formula according to DIN ISO 14728-1
Lnom = (C / P)q × 100 km
Lnom = Nominal service life (km)
C = Dynamic load capacity (N)
P = Equivalent force (N)
q = Service life calculation exponent
Roller Guideways (MR)
q = 10/3 ≈ 3.33
Line contact, higher load capacity
Ball Guideways (BM)
q = 3
Point contact, suitable for high-speed motion
Nominal Service Life Lnom
The nominal service life Lnom is the calculated travel distance that 90% of guideways operating under the same conditions can reach or exceed. This is a statistical concept representing the expected life under ideal conditions.
Unless there are other special requirements, all SCHNEEBERGER designs are based on the Lnom service life. This means that under the same conditions, 10% of guideways may reach their fatigue limit prematurely.
Service Life Comparison: Roller vs. Ball Guideways
Due to the difference in the service life exponent q, roller guideways and ball guideways have different nominal service lives at the same C/P ratio. The following figure shows the service life curves for both guideway types:
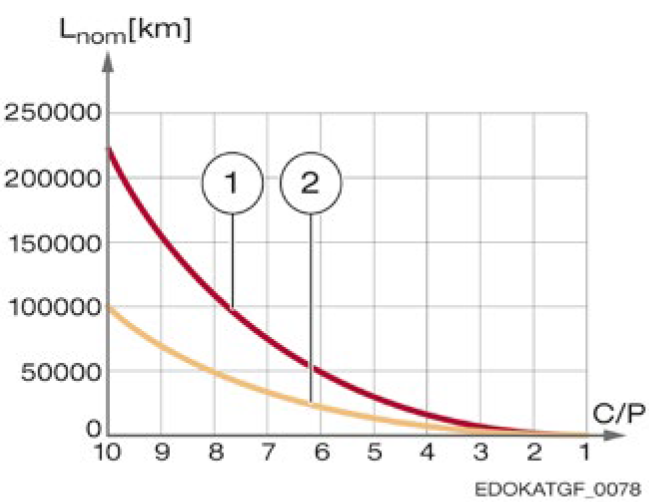
Nominal service life Lnom of roller and ball guideways as a function of the C/P ratio (without preload influence)
Legend:
Y-axis: Lnom [km] - Nominal service life (kilometers)
X-axis: C/P - Ratio of dynamic load capacity to equivalent force
Curve Interpretation
As can be seen from the figure, at the same C/P ratio, the nominal service life of roller guideways (curve 1) is significantly higher than that of ball guideways (curve 2). This is because roller guideways use line contact, which provides higher load capacity and lower contact stress. When C/P = 10, the service life of roller guideways can reach approximately 220,000 km, while ball guideways reach approximately 100,000 km.
Actual Service Life
Actual service life refers to the life actually achieved, which may differ significantly from the theoretical nominal service life. Actual service life is affected by various factors:
- Operating conditions (speed, acceleration, vibration)
- Lubrication condition (lubricant type, lubrication frequency)
- Environmental factors (temperature, humidity, contaminants)
- Installation accuracy and connecting structure rigidity
- Load variations and impact loads
1.7.2 Applicable Standards
Service life calculation as well as static and dynamic load capacities of linear guideways are detailed in the following international standards:
DIN ISO 14728-1
Rolling bearings - Linear motion rolling bearings - Part 1
Dynamic load ratings and rating life
DIN ISO 14728-2
Rolling bearings - Linear motion rolling bearings - Part 2
Static load ratings
Important Note
The calculated nominal service life is a statistical average. Actual service life may vary depending on operating conditions, lubrication status, environmental factors, etc. It is recommended to use appropriate safety factors in design. For detailed calculation methods, please refer to Section 4.10 - Calculation and Selection.