This chapter provides detailed information on the mounting methods, fastening techniques, tolerance specifications, and key factors affecting accuracy for SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL guideway systems. Proper guide rail mounting is essential for ensuring system accuracy, service life, and operating performance.
4.9.1 Methods of Attachment
MONORAIL guide rails can be fastened in two ways. Standard rails (N) and rails for cover strips (C) have continuous fixing holes with countersinks that can be fastened from above. Additionally, there are guide rails with threaded fixing holes on the bottom (U) that can be bolted from below the machine work table. The following overview shows the advantages and disadvantages of both fastening methods.
Fastening from Above (N, ND, C, CD)
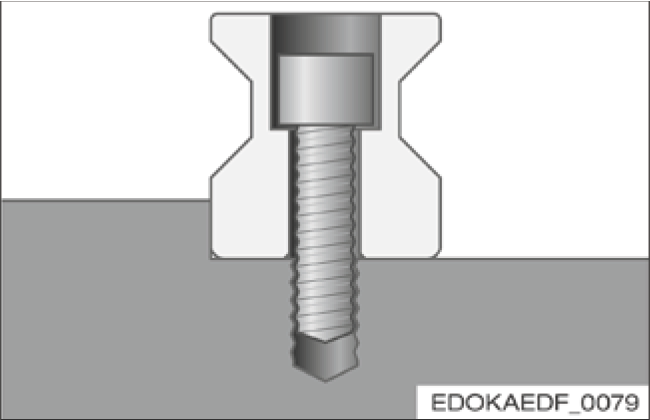
Advantages
- Easy access
Disadvantages
- Guide rail fixing holes must be closed with plugs or cover strips to protect wipers
- Protruding edges due to closures: wiper wear, contamination
Fastening from Below (NU, NUD)
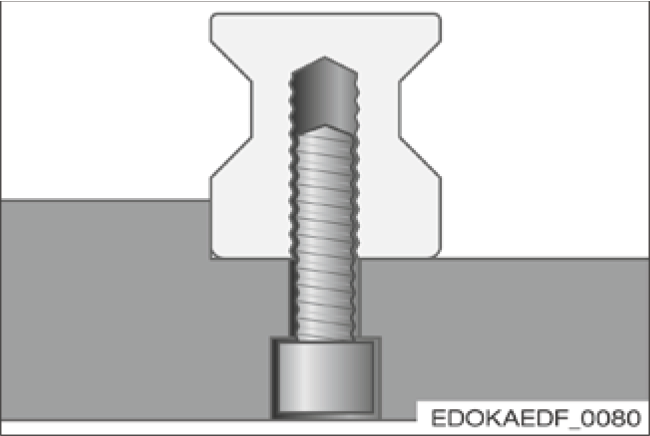
Advantages
- No closures required for guide rail fixing holes
- No protruding edges on guide rail surface
Disadvantages
- Limited accessibility
- Lower clamping force due to longer screws
4.9.2 Guide Rail Options
Special Fixing Hole Spacing L4
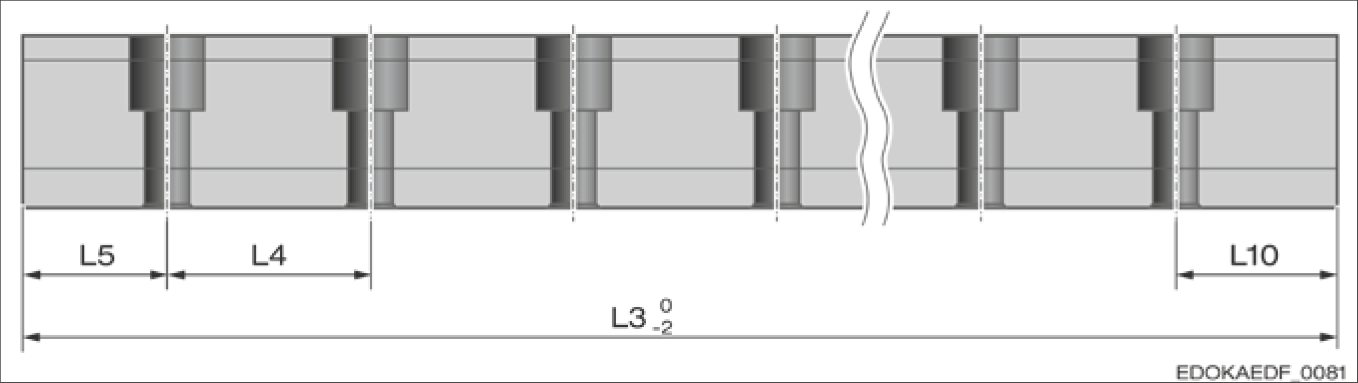
Fixing hole spacing diagram
Fixing Hole Spacing Legend:
- L5 - Starting fixing hole spacing
- L4 - Fixing hole spacing
- L3 - Guide rail length
- L10 - End fixing hole spacing
Double or Half Fixing Hole Spacing L4
Upon request, MONORAIL MR guide rails can be supplied with double fixing hole spacing L4. This is not a standard product (order code NX). Availability should be inquired. It should be noted that in this case, rigidity and running accuracy will be reduced.
For MONORAIL BM guide rails, guide rails with half fixing hole spacing (corresponding to MR standard L4) are also available to increase rigidity and improve running accuracy. This is not a standard product (order code NX). Availability should be inquired.
Other Special Fixing Hole Spacings
Customer-specific fixing hole spacings or fixing hole spacings that vary over the guide rail length, for example at joints of multi-part guide rails, are available upon request.
Additional Locating Holes and Threads
Guide rails with additional fixing holes, for example for locating pins, or with additional threaded holes are optionally available. Availability should be inquired.
Additional Fixing Holes on Guide Rail Top Surface
Additional fixing holes can be machined on the top surface of guide rails according to customer-specific specifications, for example for locating pins or through holes (e.g., for mounting carriages). Availability should be inquired.
Guide Rail End Machining
Guide rail ends are machined after separating the guide rail.
Standard Design:
- Chamfer for transferring carriages
- Prevents damage
- For guide rails with cover strips, provides clean support for cover strips
Standard
Important Note
Special guide rail options require advance planning and confirmation of feasibility and delivery time with the SCHNEEBERGER technical team. These options may affect guide rail performance characteristics, and detailed discussion during the design phase is recommended.
4.9.3 Fixing Hole Closures
The following closures are available for guide rail fixing holes:
For a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of various element types, see Section 4.3 - Guide Rail Types.
For available sizes, types, and ordering details, see the SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL and AMS product catalog; for installation information, see the SCHNEEBERGER steel plug and brass plug installation instructions.
Plastic Plugs
Features:
- Inexpensive
- Easy to install and remove
- Suitable for protected axes and clean working environments, e.g., handling applications
- Roller product order code: MRK
- Ball product order code: BRK
- Cannot be reused
Brass Plugs
Features:
- Inexpensive
- Smooth and gap-free surface
- Excellent wiping function
- Suitable for higher thermal loads and mechanical stresses
- Liquid-tight
- Assembly requires hydraulic installation tool
- Cannot be reused
- Roller product order code: MRS
- Ball product order code: BRS
Steel Plugs
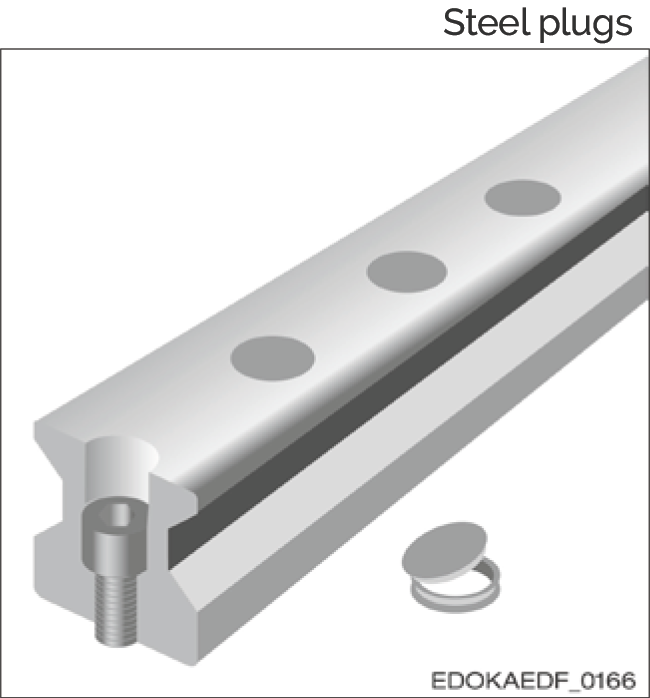

Features:
- Smooth guide rail surface
- Good wiping function
- Suitable for high mechanical and thermal stresses, e.g., outdoor environments, chip zones
- Simple assembly using hydraulic installation tool
- Expensive
- Cannot be reused
- Roller product order code: MRZ
Cover Strips
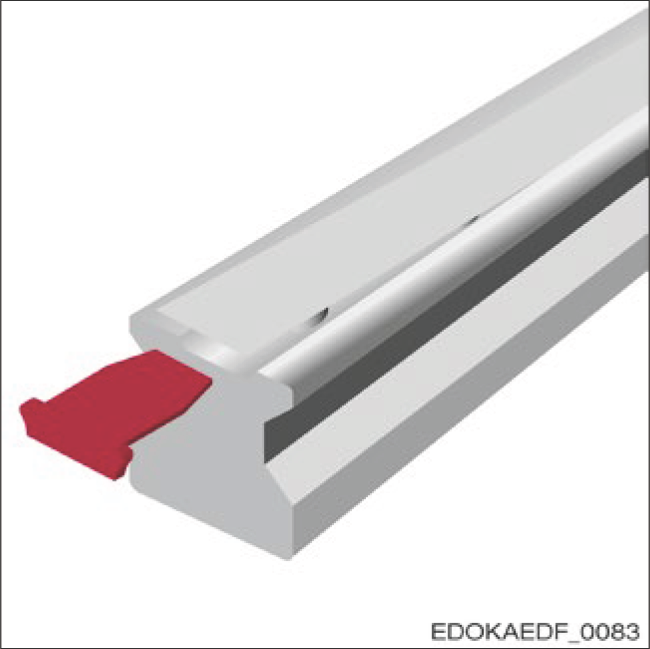

Features:
- Smooth guide rail surface with only one protruding edge in the longitudinal direction
- Good wiping function
- Minimized installation effort using installation tools
- Only one closure required for the entire guide rail
- Reusable multiple times and easy to remove
- Free space behind guide rail required for installation
- Use end pieces (EST) or fixing strips (BSC) to secure cover strip ends
- Roller product order code: MAC
- Ball product order code: BAC
4.9.4 Guide Rail Length Tolerances
The longitudinal tolerance for single-part and multi-part guide rails is: L3 = -/-2 mm
The position tolerances of fixing holes for single-part and multi-part guide rails are as follows:
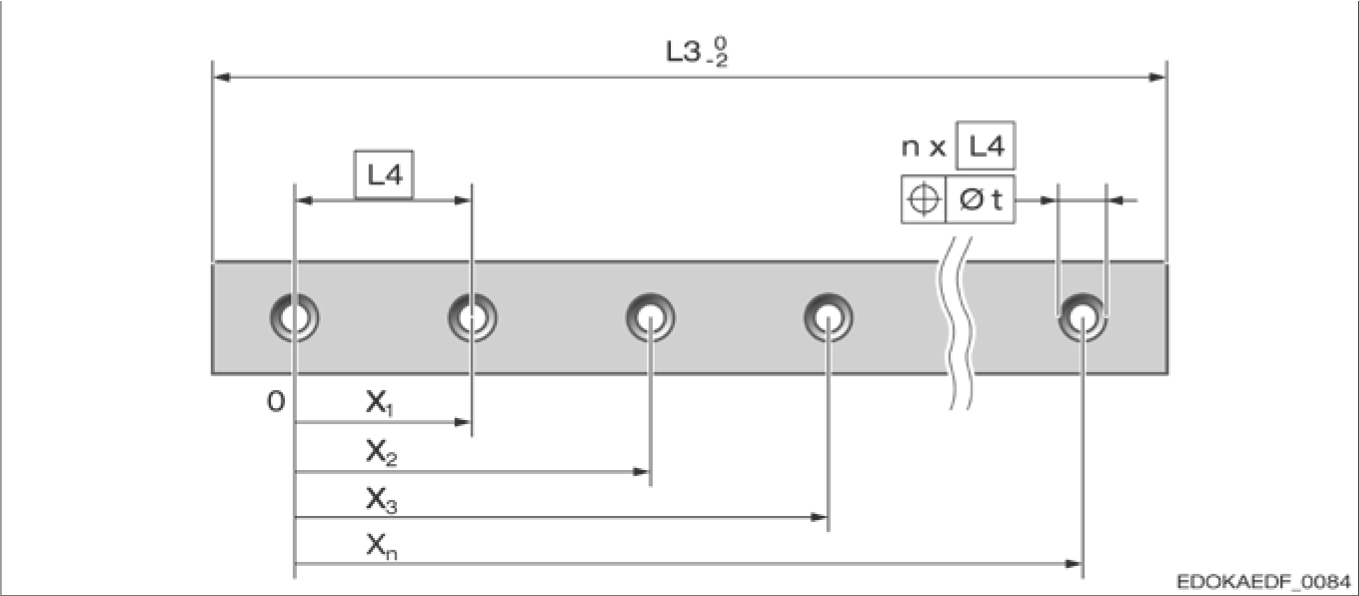
Fixing hole spacing diagram L4:
L4 = Fixing hole spacing
L3 = Guide rail length
| Position Tolerance t (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Guide Rail | xn ≤ 1000 mm | xn > 1000 mm |
| Induction hardened | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Through hardened | 0.6 | 0.8 |
4.9.5 Permissible Screw Tightening Torques
The table below lists the maximum tightening torques for DIN 912 / ISO 4762 fixing screws. This value is based on a friction coefficient μ = 0.125 in the as-delivered condition.
Caution
Components may be damaged if screws are not tightened with correct torque
- The recommendations of the screw supplier must be followed and are always binding.
- Low-head screws DIN 6912 should be tightened according to strength class 8.8.
- 8.8 grade screws should be used for AMS guide rails.
Tightening Torques for ISO 4762 Fixing Screws:
| Maximum Tightening Torque (Nm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screw | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M24 |
| Size | (15) | (20) | (25) | (30, 35) | (45) | (55) | (65) | (100) |
| Strength Class 8.8 | 3 | 6 | 10 | 24 | 83 | 130 | 200 | 700 |
| Strength Class 12.9 | 5 | 10 | 16 | 40 | 95 | 166 | 265 | 1100 |
Note
Values in parentheses in the table indicate screw lengths (mm).
4.9.6 Permissible Lateral Force Without Locating Surface
For cases where no locating surface is provided, guide values for maximum permissible lateral force can be obtained from the table below.
FSide_max values depend on the dynamic load capacity C, carriage fastening type, and screw strength class.
Note
Based on screw connections with strength class 8.8. Values in the table represent the maximum lateral force applied to a guide rail by one carriage, applicable to standard fixing hole spacing L4. Values increase correspondingly when using two or more carriages.
MONORAIL MR Maximum Lateral Force FLateral_max (N)
| Size | Carriage Type A, C, E | Carriage Type B, D |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 1400 | 1600 |
| 30 | 2800 | 3200 |
| 35 | 2800 | 3200 |
| 45 | 6900 | 7900 |
| 55 | 9600 | 10900 |
| 65 | 13200 | 15100 |
| 100 | 31500 | 36000 |
MONORAIL BM Maximum Lateral Force FLateral_max (N)
| Size | Carriage Type A, C, E, F | Carriage Type B, D, G |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 280 | 320 |
| 20 | 480 | 550 |
| 25 | 710 | 810 |
| 30 | 1400 | 1600 |
| 35 | 1400 | 1600 |
| 45 | 3400 | 3900 |
Note
For detailed values and data for other series (such as AMS), please refer to the SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL and AMS product catalog.
The maximum lateral forces listed apply only to ideally rigid connection surfaces in the connecting structure and screw fasteners made of steel or cast steel. In cases of unstable connection surfaces, screw loads will increase significantly, which may cause screw connections to loosen. For aluminum screw fasteners, maximum permissible lateral forces should be reduced according to VDI 2230 standards.
4.9.7 Permissible Tensile Forces and Lateral Torques
The maximum load on profiled rail systems is determined not only by the static load capacity C0 and static moment M0 of the rolling contacts, but also by the screw connections of the carriages and guide rails. In this case, the screw connections of the guide rails determine the maximum load limit.
Note
Based on screw connections with strength class 8.8. Values in the table represent the maximum permissible tensile force and lateral torque applied to a guide rail by one carriage, applicable to standard fixing hole spacing L4.
MONORAIL MR Maximum Tensile Force and Lateral Torque
| Size | Carriage Type A, C, E | Carriage Type B, D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTension_max (N) | MQ_max (Nm) | FTension_max (N) | MQ_max (Nm) | |
| 25 | 18800 | 200 | 21500 | 230 |
| 30 | 37000 | 490 | 42300 | 560 |
| 35 | 36900 | 590 | 42200 | 680 |
| 45 | 91700 | 1900 | 104800 | 2200 |
| 55 | 127400 | 3200 | 145600 | 3600 |
| 65 | 176400 | 5200 | 201700 | 6000 |
| 100 | 419400 | 19700 | 479300 | 22500 |
MONORAIL BM Maximum Tensile Force and Lateral Torque
| Size | Carriage Type A, C, E, F | Carriage Type B, D, G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTension_max (N) | MQ_max (Nm) | FTension_max (N) | MQ_max (Nm) | |
| 15 | 3700 | 26 | 4200 | 30 |
| 20 | 6400 | 60 | 7300 | 68 |
| 25 | 9400 | 100 | 10800 | 120 |
| 30 | 18500 | 240 | 21100 | 280 |
| 35 | 18500 | 300 | 21100 | 340 |
| 45 | 45900 | 970 | 52400 | 1100 |
Notes
When these values are exceeded, screw connections must be checked. For this purpose, you may need to loosen the screw connections.
The maximum tensile forces and torques listed apply only to ideally rigid connection surfaces in the connecting structure and screw fasteners made of steel or cast steel. In cases of unstable connection surfaces, screw loads will increase significantly, which may cause screw connections to loosen. For aluminum screw fasteners, maximum tensile forces and lateral torques should be reduced according to VDI 2230 standards.
4.9.8 Factors Affecting Accuracy
The accuracy of guide rail fastening is affected by a series of factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy of connecting structure | Surface accuracy is directly transferred to guide rail: Insufficient quality shortens service life |
| Straightness of guide rail | No kinks, in accordance with SCHNEEBERGER specifications |
| Fixing hole spacing | Screws cannot be installed on the machine bed but remain in guide rail fixing holes |
| Installation method (with/without lateral locating surface) | Limits straightness when applicable |
| Tightening torque | Ensure uniform screw tightening |
| Use of flat washers | Ensure flat washers are not positioned over fixing holes and do not limit plug installation space |
| Lubrication condition of machine bed, guide rails, and screws | Clean all components |
| Installation method (tightening screws all at once or pre-aligning at lower torque first) | See MONORAIL and AMS installation instructions |
| Tightening sequence of fixing holes | See MONORAIL and AMS installation instructions |
| Temperature difference between guide rail and machine bed during installation (thermal expansion) | Ensure guide rail and machine bed have the same temperature during installation |
Detailed Information
For detailed information on each point, see:
- SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL and AMS product catalog and installation instructions
- Section 1.6 - Accuracy
- Section 1.7 - Straightness and guide rail curvature
- Section 4.7 - Straightness