SCHNEEBERGER MONORAIL offers a variety of clamping and braking components for fixing or braking guideway systems. These components play a critical role in machine tools, automation equipment, and applications requiring precise positioning.
4.16.1 Construction and Application Areas
Construction principles, activation methods, and typical application scenarios for clamping and braking components.
Basic Construction
Clamping and braking components achieve fixing or braking functions through clamping forces acting on the guide rail. Depending on application requirements, these components can be mounted directly on the carriage or independently beside the guide rail.
Structural Types
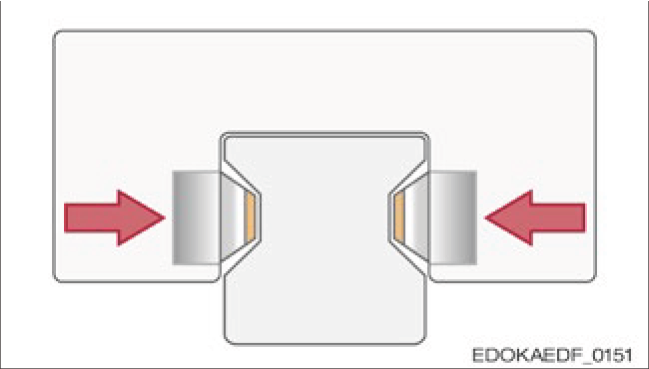
Contact area on carriage
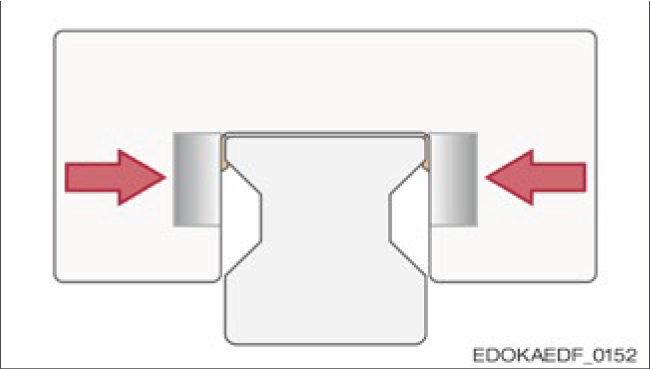
Contact area with guide rail flange. Suitable for guide rails equipped with AMS!
Application Areas
- Machine tools: Precise positioning of work tables and tools
- Automation equipment: Controlling stop positions of handling systems
- Measuring equipment: Fixing measuring platforms to ensure accuracy
- Medical equipment: Precise positioning of surgical tables and diagnostic equipment
- Semiconductor manufacturing: Precise control of wafer handling systems
4.16.2 Clamping and Braking Component Types
There are various types of stabilizing elements, which differ in function, pressure generation method, and effect.
Functional Classification
Based on function, they can be distinguished as clamping elements and braking elements. Clamping elements are used to fix idling machine axes. Braking elements are able to brake axes from motion. For this purpose, they are equipped with special slideway coatings designed so that the guide rail is not damaged.

Caution
Component damage due to braking system failure
- Braking components are designed for emergency stop situations and must not be used as operational brakes!
Pressure Medium
Distinction based on pressure generation method:
Manual
Clamping force generated through manual operation, suitable for low-frequency operation applications.
Pneumatic
Uses compressed air to generate clamping force, fast response, suitable for automation applications.
Hydraulic
Uses hydraulic oil to generate high clamping force, suitable for heavy-load applications.
Electric
Motor-driven, precise control of clamping force, suitable for applications requiring high precision.
Effect Classification
There are both active elements, i.e., elements that act by applying pressure, and passive elements, in which case their holding force is achieved through pressure drop. For these elements, the holding force is generated by an integrated spring energy storage. The pressure medium is used to release the holding force, or can be used in combination with the spring energy storage in elements with so-called positive connection to increase their holding force.
4.16.3 Type Overview
The following tables provide an overview of different types, their characteristics, and uses:
Pneumatic Clamping and Braking Component Series

Product Series Overview: HK, MK, MKS, MBPS, BWPS, TKPS, UBPS, LBPS
| Characteristic/Series | HK | MK | MKS | MBPS | BWPS | TKPS | UBPS | LBPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Medium | ||||||||
| Manual | ● | |||||||
| Pneumatic | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| Hydraulic | ||||||||
| Electric | ||||||||
| Spring Energy Storage | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| PLUS Connection | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| Braking Element | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||
| DIN 645 Compatible | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| Guide Rail Type | ||||||||
| MR Roller | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| MR with AMS | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| BM Ball | ● | ● | ● | |||||
Note: ● = Applicable
Order code: Series xx, where xx = size (e.g., "MKS xx")
Hydraulic and Electric Clamping Component Series
Product Series Overview: KWH, KBH, KBHS, MKE
| Characteristic/Series | KWH | KBH | KBHS | MKE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Medium | ||||
| Manual | ||||
| Pneumatic | ||||
| Hydraulic | ● | ● | ● | |
| Electric | ● | |||
| Spring Energy Storage | ● | |||
| PLUS Connection | ||||
| Braking Element | ● | ● | ||
| DIN 645 Compatible | ● | ● | ||
| Guide Rail Type | ||||
| MR Roller | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| MR with AMS | ||||
| BM Ball | ● | |||
Note: ● = Applicable
Order code: Series xx, where xx = size (e.g., "MKS xx")