AM Ball Screws - Lead Accuracy
Lead Accuracy - Type T and Type P
Lead Accuracy Concept
According to ISO/DP 3408/3, concepts, names, and tolerances are distinguished as: nominal lead, specified lead, and actual lead.
A straight line is determined from the actual lead gradient. Tolerance lines run parallel to this straight line.
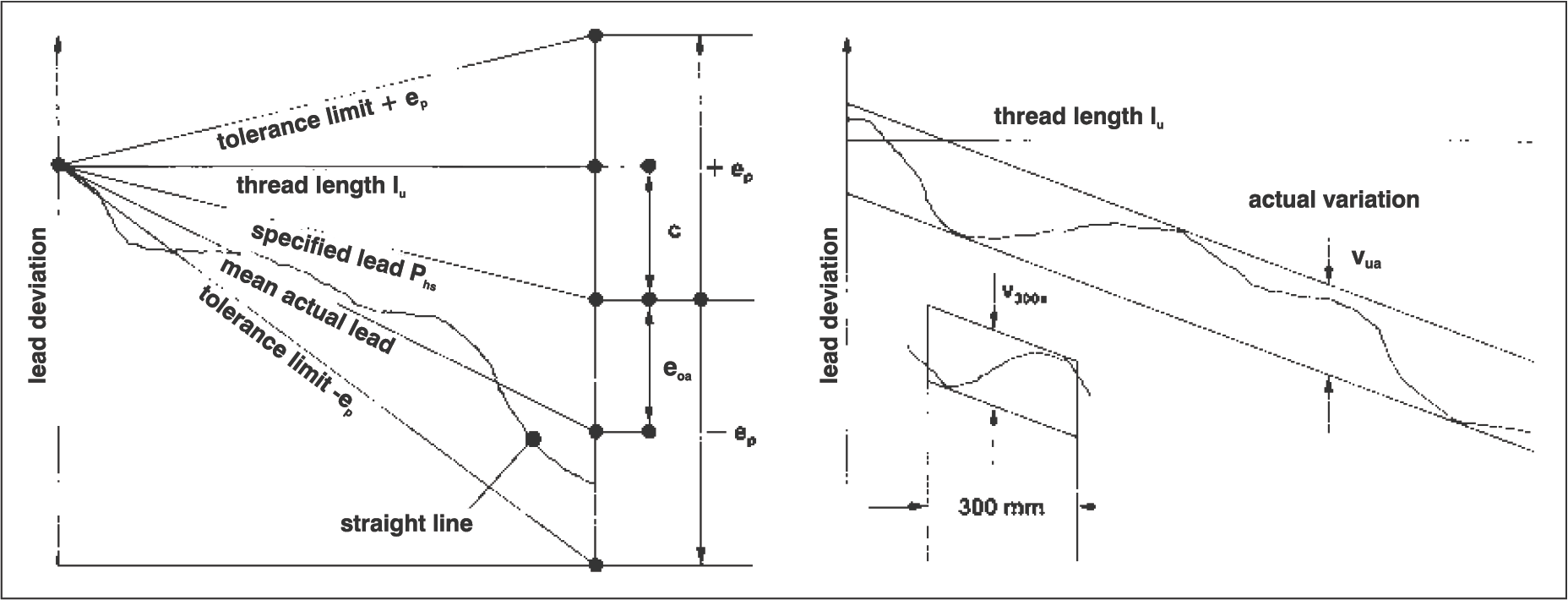
To compensate for length changes of the screw due to thermal expansion and/or preload, the user must specify the specified lead or c= value (compensation), giving the difference between specified lead and nominal lead. All deviations e then relate to the specified lead.
Lead Accuracy Parameters
Subscript a: Actual values, most important:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| epa | Mean actual lead deviation related to usable thread length Iu |
| v300a | Actual variation within 300 mm range |
| vua | Actual variation within Iu range |
Subscript p: Permissible values, most important:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| epp | Permissible mean lead deviation related to Iu |
| e1000p | Permissible mean lead deviation within 1000 mm range |
| v300p | Permissible variation within 300 mm range |
| vup | Permissible variation within Iu range |
These tolerance limits are specified by length in accuracy grades.
Type T (Transmission)
Type T (Transmission)
| v300p (µm) | ±e1000p (µm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT 1 | IT 3 | IT 5 | IT 1 | IT 3 | IT 5 |
| 6 | 12 | 23 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
When a parallel measuring system (such as a linear scale or position sensor) is present, the ball screw's function is limited to feed motion. In this case, the screw lead is not used as a distance measurement reference, and accuracy requirements are mainly variation requirements.
Therefore, Type T (T=Transmission) lead accuracy is used for "direct" measuring systems.
Type P (Positioning)
Type P (Positioning)
| Thread length | vup (µm) | ±ep (µm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT 1 | IT 3 | IT 5 | IT 1 | IT 3 | IT 5 | ||
| from | to | ||||||
| ≦315 | 6 | 12 | 23 | ||||
| 316 | 400 | 6 | 12 | 25 | 7 | 13 | 25 |
| 401 | 500 | 7 | 13 | 26 | 8 | 15 | 27 |
| 501 | 630 | 7 | 14 | 29 | 9 | 16 | 30 |
| 631 | 800 | 8 | 16 | 31 | 10 | 18 | 35 |
| 801 | 1000 | 9 | 17 | 35 | 11 | 21 | 40 |
| 1001 | 1250 | 10 | 19 | 39 | 13 | 24 | 46 |
| 1251 | 1600 | 11 | 22 | 44 | 15 | 29 | 54 |
| 1601 | 2000 | 13 | 25 | 51 | 18 | 35 | 65 |
| 2001 | 2500 | 15 | 29 | 59 | 22 | 41 | 77 |
| 2501 | 3150 | 17 | 34 | 69 | 26 | 50 | 93 |
| 3151 | 4000 | 21 | 41 | 82 | 32 | 62 | 115 |
| 4001 | 5000 | 25 | 50 | 99 | 39 | 76 | 140 |
When a shaft encoder on the screw or motor center line indicates position (distance) increments in angular steps, the ball screw lead must have the highest accuracy because it has become an important part of the table travel measurement.
This also applies to incremental motor applications. Such applications using "indirect" measuring systems require Type P (P=Positioning) because the screw with travel length represents an absolute length standard.
Accuracy Grade Selection Guide
| Accuracy Type | Application Scenario | Measuring System |
|---|---|---|
| Type T | Feed motion, accuracy guaranteed by external measuring system | Direct measurement (linear scale, position sensor) |
| Type P | Precision positioning, lead used as position reference | Indirect measurement (shaft encoder, incremental motor) |
Selection Recommendation: When using direct measuring systems such as linear encoders, Type T can be selected to reduce costs. When the screw lead is used as a positioning reference, Type P must be selected to ensure accuracy.